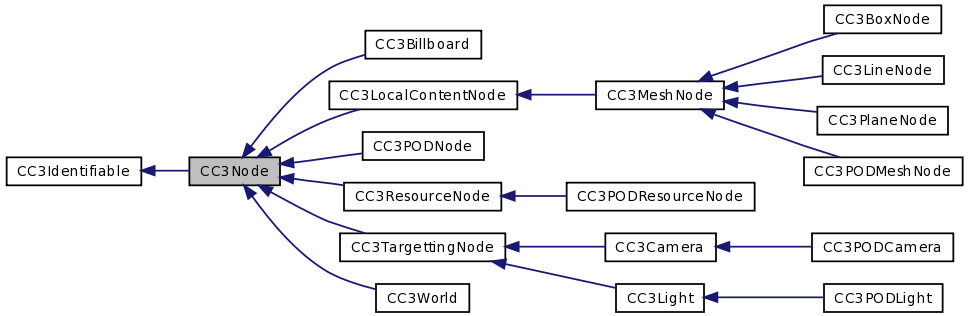
CC3Node and its subclasses form the basis of all 3D artifacts in the 3D world, including visible meshes, structures, cameras, lights, resources, and the 3D world itself. More...
#import <CC3Node.h>
Detailed Description
CC3Node and its subclasses form the basis of all 3D artifacts in the 3D world, including visible meshes, structures, cameras, lights, resources, and the 3D world itself.
Nodes can be moved, rotated and scaled. Rotation can be specified via either Euler angles or quaternions.
Nodes can be assembled in a structural hierarchy of parents and children, and transformations that are applied to a node are also applied to its descendant nodes. Typically, the root of a structural node hierarchy is an instance of CC3World.
Each node is automatically touched at two distinct times during animation frame handling. First, the updateBeforeTransform: and updateAfterTransform: methods are each invoked during scheduled model state updating, before and after the transformation matrix of the node is rebuilt, respectively. You should override udpateBeforeTransform: method to make any changes to the node, or its child nodes.
You should override updateAfterTransform: only if you need to make use of the global properties of the node or its child nodes, such as globalLocation, globalRotation, or globalScale. These properties are valid only after the transformMatrix has been calculated, and are therefore not valid within the updateBeforeTransform: method. However, if you make any changes to the transform properties (location, rotation, scale) of a node within the updateAfterTransform: method, you must invoke the updateTransformMatrices method on that node in order to have the changes applied to the node's transformMatrix.
Note that you do NOT need to invoke the updateTransformMatrices method for any changes made in the updateBeforeTransform: method, since those changes will automatically be applied to the transformMatrix.
The second place a node is touched is, the drawWithVisitor: method, which is automaticaly invoked during each frame rendering cycle. You should have no need to override this method.
To maximize throughput, the operations of updating model state should be kept separate from the operations of frame rendering, and the two should not be mixed. Subclasses should respect this design pattern when overriding behaviour. Drawing operations should not be included in state updating, and vice versa. Since OpenGL is a hardware-accelerated state-machine pipeline, this separation allows frame-drawing operations to be performed by the GPU at the same time that state update operations for the next frame are being handled by the CPU, and on some systems, permits frame drawing and model updating to be perfomed on separate threads.
CC3Nodes support the cocos2d CCAction class hierarchy. Nodes can be translated, rotated, and scaled in three dimensions, or made to point towards a direction (for cameras and lights), all under control of cocos2d CCActions. As with other CCActions, these actions can be combined into action sequences or repeating actions, or modified with cocos2d ease actions. See the class CC3TransformTo and its subclasses for actions that operate on CC3Nodes.
When populating your world, you can easily create hordes of similar nodes using the copy and copyWithName: methods. Those methods effect deep copies to allow each copy to be manipulated independently, but will share underlying mesh data for efficient memory use. See the notes at the copy method for more details about copying nodes.
You can animate this class with animation data held in a subclass of CC3NodeAnimation. To animate this node using animation data, set the animation property to an instance of a subclass of the abstract CC3NodeAnimation class, populated with animation data, and then create an instance of a CC3Animate action, and run it on this node.
To maximize GL throughput, all OpenGL ES 1.1 state is tracked by the singleton instance [CC3OpenGLES11Engine engine]. CC3OpenGLES11Engine only sends state change calls to the GL engine if GL state really is changing. It is critical that all changes to GL state are made through the CC3OpenGLES11Engine singleton. When adding or overriding functionality in this framework, do NOT make gl* function calls directly if there is a corresponding state change tracker in the CC3OpenGLES11Engine singleton. Route the state change request through the CC3OpenGLES11Engine singleton instead.
Member Function Documentation
| - (void) addAndLocalizeChild: | (CC3Node *) | aNode |
Adds the specified node as a direct child node to this node, and localizes the child node's location, rotation, and scale properties to this node.
This has the effect of leaving the global location, rotation and scale of the child node as they were, but re-homing the node to this parent. Visually, the node appears to stay in place, but will now move with the new parent, not with the old parent.
For instance, you might have an apple object whose overall intended global size and orientation you know, but you want that object to be added to a bowl, so that when you move the bowl, the apple moves with it. The bowl has likely been rotated and scaled, and raised onto a table, and you don't want your known apple to be transformed by the table and bowl when you add the apple to the bowl, You can use this method on the bowl object to add the apple, and reverse the table and bowl transforms for the apple, so that the apple will appear with its current size and orientation.
To do this, this method finds the appropriate location, rotation, and scale properties for the child node that will result in the globalLocation, globalRotation and globalScale properties remaining the same after it has been added to this parent node.
The child node is removed from its existing parent.
| - (void) addChild: | (CC3Node *) | aNode |
Adds the specified node as a direct child node to this node.
The child node is first removed from its existing parent.
| - (void) checkDrawingOrder |
Checks that the child nodes of this node are in the correct drawing order relative to other nodes.
This implementation forwards this request to all descendants. Those descendants with local content to draw will check their positions in the drawing sequence by passing this notification up the ancestor chain to the CC3World.
By default, nodes are automatically repositioned on each drawing frame to optimize the drawing order, so you should usually have no need to use this method.
However, in order to eliminate the overhead of checking each node during each drawing frame, you can disable this automatic behaviour by setting the allowSequenceUpdates property of specific drawing sequencers to NO.
In that case, if you modify the properties of a node or its content, such as mesh or material opacity, and your CC3World drawing sequencer uses that criteria to sort nodes, you can invoke this method to force the node to be repositioned in the correct drawing order.
You don't need to invoke this method when initially setting the properties. You only need to invoke this method if you modify the properties after the node has been added to the CC3World, either by itself, or as part of a node assembly.
Implemented in CC3LocalContentNode.
| - (id) copy |
Returns a newly allocated (retained) copy of this instance.
The new copy will have the same name as this node, but will have a unique tag.
The copying operation effects a deep copy. For any content that is held by reference (eg- objects), and subject to future modification, a copy is created, so that both this instance and the other instance can be treated independently. This includes child nodes, of which copies are created.
The following rules are applied when copying a node:
- The tag property is not copied. The tag is property is assigned and automatically generated unique tag value.
- The copy will initially have no parent. It will automatically be set when this node is added as a child to a parent node.
- Copies are created of all child nodes, using the copy method of each child. The child nodes of the new node will therefore have the same names as the child nodes of the original node.
- Mesh data is copied by reference, not by value. Child nodes that support mesh data will assign it by reference when that child is copied. Mesh data is shared between both the original mesh node and copy node.
Subclasses that extend content should honour the deep copy design pattern, making exceptions only for content that is both large and not subject to modifications, such as mesh data.
This method may often be used to duplicate a node many times, to create large number of similar instances to populate a game. To help you verify that you are correctly releasing and deallocating all these copies, you can use the instanceCount class method to get a current count of the total number of instances of all subclasses of CC3Identifiable, When reviewing that number, remember that nodes are only one type of CC3Identifiable, and other subclasses, such as materials, will contribute to this count.
Implements CC3Identifiable.
| - (id) copyWithName: | (NSString *) | aName |
Returns a newly allocated (retained) copy of this instance.
The new copy will have its name set to the specified name, and will have a unique tag.
The copying operation effects a deep copy. See the notes at the copy method for more details about copying nodes.
Implements CC3Identifiable.
| - (void) createGLBuffers |
Creates OpenGL ES buffers to be used by the GL engine hardware.
Default behaviour is to invoke the same method on all child nodes. Subclasses that can make use of hardware buffering, notably mesh subclasses, will override and bind their data to GL hardware buffers.
Invoking this method is optional and is not performed automatically. If an application does not wish to use hardware buffering for some nodes, it can do so by avoiding the invocation of this method on those nodes. Typically, however, an applicaiton will simply invoke this method once during initialization of highest-level ancestor node (ususally a subclass of CC3World).
| - (void) deleteGLBuffers |
Deletes any OpenGL buffers that were created by any child nodes via a prior invocation of createGLBuffers.
If the child nodes also retained the data locally, drawing will then revert to distinct GL draw calls, passing data through the GL API on each call, rather than via the bound buffers.
| - (void) disableAllAnimation |
Disables animation of this node, and all descendant nodes, from animation data held in the animation property of this node and each descendant node.
| - (void) disableAnimation |
Disables animation of this node from animation data held in the animation property.
This will not disable animation of child nodes.
| - (BOOL) doesIntersectFrustum: | (CC3Frustum *) | aFrustum |
Returns whether the local content of this node intersects the given frustum.
This check does not include checking children, only the local content.
This method is called during the drawing operations of each frame to determine whether this node should be culled from the visible nodes and not drawn. A return value of YES will cause the node to be drawn, a return value of NO will cause the node to be culled and not drawn.
Culling nodes that are not visible to the camera is an important performance enhancement. The node should strive to be as accurate as possible in returning whether it intersects the camera's frustum. Incorrectly returning YES will cause wasted processing within the GL engine. Incorrectly returning NO will cause a node that should at least be partially visible to not be drawn.
In this implementation, if this node has a boundingVolume, this method delegates to it. Otherwise, it simply returns YES. Subclasses may override to change this standard behaviour.
| - (void) drawWithVisitor: | (CC3NodeDrawingVisitor *) | visitor |
Draws or applies this node to the GL engine.
The specified visitor encapsulates the frustum of the currently active camera, and certain drawing options.
To avoid unnecessary drawing operations, this node will only be drawn if the node:
- is visible (as indicated by the visible property)
- has content to draw (as indicated by the hasLocalContent property)
- intersects the camera's frustum (which is checked by invoking the method doesIntersectFrustum: of this node with the frustum from the visitor).
If all of these tests pass, drawing is required, and this method transforms and draws the local content of this node.
If this node is visible and the visitor indicates that children should also be drawn, this method then passes this notificaton along to the child nodes.
As described in the class documentation, in keeping with best practices, drawing and frame rendering should be kept separate from updating the model state. Therefore, when overriding this method in a subclass (or any of the template methods invoked by this method), do not update any model state. This method should perform only frame rendering operations.
| - (void) enableAllAnimation |
Enables animation of this node, and all descendant nodes, from animation data held in the animation property of this node and each descendant node.
| - (void) enableAnimation |
Enables animation of this node from animation data held in the animation property.
This will not enable animation of child nodes.
| - (void) establishAnimationFrameAt: | (ccTime) | t |
Updates the location, rotation and scale of this node based on the animation frame located at the specified time, which should be a value between zero and one, with zero indicating the first animation frame, and one indicating the last animation frame.
Only those properties of this node for which there is animation data will be changed.
This implementation delegates to the CC3NodeAnimation instance held in the animation property, then passes this notification along to child nodes to align them with the same animation frame. Linear interpolation of the frame data may be performed, based on the number of frames and the specified time.
If disableAnimation or disableAllAnimation has been invoked on this node, it will be excluded from animation, and this method will not have any affect on this node. However, this method will be propagated to child nodes.
This method is invoked automatically from an instance of CC3Animate that is animating this node. Usually, the application never needs to invoke this method directly.
| - (NSArray*) flatten |
Returns an autoreleased array containing this node and all its descendants.
This is done by invoking flattenInto: with a newly-created array, and returning the array.
| - (void) flattenInto: | (NSMutableArray *) | anArray |
Adds this node to the specified array, and then invokes this method on each child node.
The effect is to populate the array with this node and all its descendants.
| - (CCAction*) getActionByTag: | (int) | tag |
Gets an action from the running action list given its tag.
| - (CC3Node*) getNodeNamed: | (NSString *) | aName |
Retrieves the first node found with the specified name, anywhere in the structural hierarchy of descendants of this node (not just direct children).
The hierarchy search is depth-first.
| - (CC3Node*) getNodeTagged: | (GLuint) | aTag |
Retrieves the first node found with the specified tag, anywhere in the structural hierarchy of descendants of this node (not just direct children).
The hierarchy search is depth-first.
| - (void) linkToPODNodes: | (NSArray *) | nodeArray |
Create links to the nodes in the specified array.
This implementation attaches this node to its parent as identified by the podParentIndex property. Subclasses may override to perform other linking.
| - (void) markTransformDirty |
Indicates that the transformation matrix is dirty and needs to be recalculated.
This method is invoked automatically as needed. Usually the application never needs to invoke this method directly.
| + (id) node |
Allocates and initializes an autoreleased unnamed instance with an automatically generated unique tag value.
The tag value is generated using a call to nextTag.
| + (id) nodeAtIndex: | (int) | aPODIndex | |
| fromPODResource: | (CC3PODResource *) | aPODRez | |
Allocates and initializes an autoreleased instance from the data of this type at the specified index within the specified POD resource.
| - (PODStructPtr) nodePODStructAtIndex: | (uint) | aPODIndex | |
| fromPODResource: | (CC3PODResource *) | aPODRez | |
Returns the underlying SPODNode data structure from the specified resource, for the SPODNode at the specified index.
The returned pointer must be cast to SPODNode before accessing any internals of the data structure.
| + (id) nodeWithName: | (NSString *) | aName |
Allocates and initializes an autoreleased instance with the specified name and an automatically generated unique tag value.
The tag value is generated using a call to nextTag.
| + (id) nodeWithTag: | (GLuint) | aTag |
Allocates and initializes an unnamed autoreleased instance with the specified tag.
| + (id) nodeWithTag: | (GLuint) | aTag | |
| withName: | (NSString *) | aName | |
Allocates and initializes an autoreleased instance with the specified tag and name.
| - (int) numberOfRunningActions |
Returns the numbers of actions that are running plus the ones that are scheduled to run (actions in actionsToAdd and actions arrays).
Composable actions are counted as 1 action. Example: If you are running 1 Sequence of 7 actions, it will return 1. If you are running 7 Sequences of 2 actions, it will return 7.
| - (void) releaseRedundantData |
Once the elements data has been buffered into a GL vertex buffer object (VBO) within the GL engine, via the createGLBuffer method, this method can be used to release the data in main memory that is now redundant from all meshes that have been buffered to the GL engine.
Invoking this method on a node will release from main memory any data within all descendant mesh nodes, that has successfully been copied to buffers in the GL engine. It is safe to invokde this method even if createGLBuffer has not been invoked, and even if VBO buffering was unsuccessful.
To exempt vertex location data from release, invoke the retainLocation method once before invoking this method. For example, sophisticated physics engines and collision detection algorithms may make use of vertex location data in main memory.
To exempt other vertex data, such as normal or texture coordinate data, from release, set the shouldReleaseRedundantData property of the appropriate vertex array to NO, prior to invoking this method.
| - (void) remove |
Convenience method that removes this node from its structural hierarchy by simply invoking removeChild: on the parent of this node.
| - (void) removeAllChildren |
Removes all child nodes of this node.
| - (void) removeChild: | (CC3Node *) | aNode |
Removes the specified node as a direct child node to this node.
Does nothing if the specified node is not actually a child of this node.
| - (void) retainVertexLocations |
Convenience method to cause the vertex location data to be retained in application memory when releaseRedundantData is invoked, even if it has been buffered to a GL VBO.
This effectively causes vertex location data to be ignored during any subsequent invocation of the releaseRedundantData method, even if it has been buffered to a GL VBO.
Some sophisticated physics engines and collision detection algorithms may make use of vertex location data in main memory, and this method can be used to ensure that such data is retained, even when other vertex data is released so save application memory.
Only the vertex location will be retained. Any other vertex data, such as normals, or texture coordinates, that has been buffered to GL VBO's, will be released from application memory when releaseRedundantData is invoked.
If you also want to retain other vertex data, you can set the shouldReleaseRedundantData property to NO on the associated vertex arrays.
| - (CCAction*) runAction: | (CCAction *) | action |
Executes an action, and returns the action that is executed.
The node becomes the action's target.
| - (void) stopAction: | (CCAction *) | action |
Removes an action from the running action list.
| - (void) stopActionByTag: | (int) | tag |
Removes an action from the running action list given its tag.
| - (void) stopAllActions |
Removes all actions from the running action list.
| - (void) touchDisableAll |
Sets the isTouchEnabled property to NO on this node and all descendant nodes.
This is a convenience method that will make this node and all its decendants unresponsive to touches. For more info see the notes for the isTouchEnabled and touchableNode properties.
| - (void) touchEnableAll |
Sets the isTouchEnabled property to YES on this node and all descendant nodes.
This is a convenience method that will make all descendants individually touchable and selectable, which is not usually what is wanted. Usually, you would set isTouchEnabled on specific parent nodes that are of interest to select a sub-assembly as a whole. However, making all components individually selectable can sometimes be desired, and is useful for testing.
For more info see the notes for the isTouchEnabled and touchableNode properties.
This is a convenience method that can find use in testing, where it might be of interest to be able to individually select small components of a larger assembly.
| - (void) updateAfterTransform: | (CC3NodeUpdatingVisitor *) | visitor |
This template method is invoked periodically whenever the 3D nodes are to be updated.
This method provides this node with an opportunity to perform update activities after the transformMatrix of the node has been recalculated. The similar and complimentary method updateBeforeTransform: is automatically invoked before the transformMatrix has been recalculated.
The global transform properties of a node (globalLocation, globalRotation, globalScale) will have accurate values when this method is run, since they are only valid after the transformMatrix has been updated. If you need to make use of the global properties of a node (such as for collision detection), override this method.
Since the transformMatrix has already been updated when this method is invoked, if you override this method and make any changes to the transform properties (location, rotation, scale) of any node, you should invoke the updateTransformMatrices method of that node, to have its transformMatrix, and those of its child nodes, recalculated.
This abstract template implementation does nothing. Subclasses that need access to their global transform properties will override accordingly. Subclasses that override do not need to invoke this superclass implementation. Nor do subclasses need to invoke this method on their child nodes. That is performed automatically.
The specified visitor encapsulates the CC3World instance, to allow this node to interact with other nodes in its world.
The visitor also encapsulates the deltaTime, which is the interval, in seconds, since the previous update. This value can be used to create realistic real-time motion that is independent of specific frame or update rates. Depending on the setting of the maxUpdateInterval property of the CC3World instance, the value of dt may be clamped to an upper limit before being passed to this method. See the description of the CC3World maxUpdateInterval property for more information about clamping the update interval.
As described in the class documentation, in keeping with best practices, updating the model state should be kept separate from frame rendering. Therefore, when overriding this method in a subclass, do not perform any drawing or rending operations. This method should perform model updates only.
This method is invoked automatically at each scheduled update. Usually, the application never needs to invoke this method directly.
| - (void) updateBeforeTransform: | (CC3NodeUpdatingVisitor *) | visitor |
This template method is invoked periodically whenever the 3D nodes are to be updated.
This method provides this node with an opportunity to perform update activities before any changes are applied to the transformMatrix of the node. The similar and complimentary method updateAfterTransform: is automatically invoked after the transformMatrix has been recalculated. If you need to make changes to the transform properties (location, rotation, scale) of the node, or any child nodes, you should override this method to perform those changes.
The global transform properties of a node (globalLocation, globalRotation, globalScale) will not have accurate values when this method is run, since they are only valid after the transformMatrix has been updated. If you need to make use of the global properties of a node (such as for collision detection), override the udpateAfterTransform: method instead, and access those properties there.
This abstract template implementation does nothing. Subclasses that act predictively, such as those undergoing trajectories or IPO curves can update their properties accordingly. Subclasses that override do not need to invoke this superclass implementation. Nor do subclasses need to invoke this method on their child nodes. That is performed automatically.
The specified visitor encapsulates the CC3World instance, to allow this node to interact with other nodes in its world.
The visitor also encapsulates the deltaTime, which is the interval, in seconds, since the previous update. This value can be used to create realistic real-time motion that is independent of specific frame or update rates. Depending on the setting of the maxUpdateInterval property of the CC3World instance, the value of dt may be clamped to an upper limit before being passed to this method. See the description of the CC3World maxUpdateInterval property for more information about clamping the update interval.
As described in the class documentation, in keeping with best practices, updating the model state should be kept separate from frame rendering. Therefore, when overriding this method in a subclass, do not perform any drawing or rending operations. This method should perform model updates only.
This method is invoked automatically at each scheduled update. Usually, the application never needs to invoke this method directly.
| - (void) updateTransformMatrices |
Applies the transform properties (location, rotation, scale) to the transformMatrix of this node, and all descendent nodes.
This method is invoked automatically during scheduled update processing between the invocations of the updateBeforeTransform: and updateAfterTransform: methods.
Changes that you make to the transform properties within the updateBeforeTransform: method will automatically be applied to the transformMatrix of the node. Because of this, it's best to make any changes to the transform properties in that method.
However, if you need to make changes to the transform properties in the updateAfterTransform: method of a node, after you have made all your changes to the node properties, you should then invoke this updateTransformMatrices method on the node, in order to have those changes applied to the transformMatrix.
Property Documentation
- (ccColor4F) ambientColor [read, write, assign] |
The ambient color of the materials of this node.
Setting this property sets the same property on all child nodes.
Querying this property returns the average value of querying this property on all child nodes. When querying this value on a large node assembly, be aware that this may be time-consuming.
Implemented in CC3Light, and CC3MeshNode.
- (CC3NodeAnimation *) animation [read, write, retain] |
The animation content of this node, which manages animating the node under the direction of a CC3Animate action.
To animate this node, set this property to an instance of a subclass of the abstract CC3NodeAnimation class, populated with animation data, and then create an instance of a CC3Animate action, and run it on this node.
- (CC3NodeBoundingVolume *) boundingVolume [read, write, retain] |
The bounding volume of this node.
This may be used by culling during drawing operations, or by physics simulations. Different shapes of boundaries are available, permitting tradeoffs between accuracy and computational processing time.
By default, nodes do not have a bounding volume. Subclasses may set a suitable bounding volume.
- (NSArray*) children [read, assign] |
The child nodes of this node, in a node structural hierarchy.
- (ccColor3B) color [read, write, assign] |
Implementation of the CCRGBAProtocol color property.
Setting this property sets the same property on all child nodes.
Querying this property returns the average value of querying this property on all child nodes. When querying this value on a large node assembly, be aware that this may be time-consuming.
Implemented in CC3MeshNode.
- (BOOL) containsAnimation [read, assign] |
Indicates whether this node, or any of its descendants, contains an instance of an animation.
- (ccColor4F) diffuseColor [read, write, assign] |
The diffuse color of the materials of this node.
Setting this property sets the same property on all child nodes.
Querying this property returns the average value of querying this property on all child nodes. When querying this value on a large node assembly, be aware that this may be time-consuming.
Implemented in CC3Light, and CC3MeshNode.
- (ccColor4F) emissionColor [read, write, assign] |
The emission color of the materials of this node.
Setting this property sets the same property on all child nodes.
Querying this property returns the average value of querying this property on all child nodes. When querying this value on a large node assembly, be aware that this may be time-consuming.
Implemented in CC3MeshNode.
- (CC3Vector) globalLocation [read, assign] |
The location of the node in 3D space, relative to the global origin.
This is calculated by using the transformMatrix to translate the global origin (0,0,0).
- (CC3Vector) globalRotation [read, assign] |
Returns the overall rotation of the node in 3D space, relative to the global X, Y & Z axes.
The returned value contains three Euler angles, specified in degrees, defining a global rotation of this node around the X, Y and Z axes.
- (CC3Vector) globalScale [read, assign] |
The scale of the node in 3D space, relative to the global coordinate system, and accumulating the scaling of all ancestor nodes.
- (BOOL) hasLocalContent [read, assign] |
Indicates whether this node has local content that will be drawn.
Default value is NO. Subclasses that do draw content will override to return YES.
- (BOOL) isAnimationEnabled [read, write, assign] |
Indicates whether animation is enabled for this node.
This property only has effect if there the animation property is not nil.
The value of this property only applies to this node, not its child nodes. Child nodes that have this property set to YES will be animated even if this node has this property set to NO, and vice-versa.
Use the methods enableAllAnimation and disableAllAnimation to turn animation on or off for all the nodes in a node assembly.
The initial value of this property is YES.
- (BOOL) isBasePODNode [read, assign] |
Indicates whether this POD is a base node, meaning that it has no parent.
- (BOOL) isMeshNode [read, assign] |
Indicates whether this node has 3D mesh data to be drawn.
Default value is NO. Subclasses that do draw 3D meshes will override to return YES.
- (BOOL) isOpaque [read, write, assign] |
Indicates whether the content of this node and its descendants is opaque.
Returns NO if at least one descendant is not opaque, as determined by its isOpaque property. Returns YES if all descendants return YES from their isOpaque property.
Setting this property sets the same property in all descendants. See the notes for this property on CC3Material for more information on how this property interacts with the other material properties.
Setting this property should be thought of as a convenient way to switch between the two most common types of blending combinations. For finer control of blending, set specific blending properties on the CC3Material instance directly, and avoid making changes to this property.
Implemented in CC3MeshNode.
- (BOOL) isTouchable [read, assign] |
Indicates whether this node can be selected by a UI touch event.
It is touchable if the isTouchEnabled property of this node, or any ancestor node is set to YES.
- (BOOL) isTouchEnabled [read, write, assign] |
Indicates if this node, or any of its descendants, can be selected by UI touch events.
This property also affects which node will be returned by the touchableNode property. If the isTouchEnabled property is explicitly set for a parent node, but not for a child node, both the parent and the child will be touchable, but it will be the parent that is returned by the touchableNode property of either the parent or child.
This design simplifies identifying the node that is of interest when a touch event occurs. Thus, a car may be drawn as a node assembly of many descendent nodes (doors, wheels, body, etc). If isTouchEnabled is set for the car structural node, but not each wheel, it will be the parent car node that will be returned by the touchableNode property of the car structural node, or each wheel node. This allows the user to touch a wheel, but still have the car identified as the object of interest.
Only visible nodes can be touched.
The initial value of this property is NO.
- (BOOL) isTransformDirty [read, assign] |
Indicates whether any of the transform properties, location, rotation, or scale have been changed, and so the transformMatrix of this needs to be recalculated.
This property is automatically set to YES when one of those properties have been changed, and is reset to NO once the transformMatrix has been recalculated.
Recalculation of the transformMatrix occurs automatically when the node is updated.
- (BOOL) isTransformRigid [read, assign] |
Indicates whether the current transform applied to this node transform is rigid, meaning that it includes only rotation and translation transformations, and does not include any scaling transformations.
This takes into consideration the transforms of all ancestors.
- (BOOL) isUniformlyScaledGlobally [read, assign] |
Indicates whether current global scaling (via the globalScale property) is uniform along all axes.
This takes into consideration the scaling of all ancestors.
- (BOOL) isUniformlyScaledLocally [read, assign] |
Indicates whether current local scaling (via the scale property) is uniform along all axes.
This does not take into consideration the scaling of any ancestors.
- (CC3Vector) location [read, write, assign] |
The location of the node in 3D space, relative to the parent of this node.
The global location of the node is therefore a combination of the global location of the parent of this node and the value of this location property.
- (GLubyte) opacity [read, write, assign] |
Implementation of the CCRGBAProtocol opacity property.
Querying this property returns the average value of querying this property on all child nodes. When querying this value on a large node assembly, be aware that this may be time-consuming.
Setting this property sets the same property in all descendants. See the notes for this property on CC3Material for more information on how this property interacts with the other material properties.
Setting this property should be thought of as a convenient way to switch between the two most common types of blending combinations. For finer control of blending, set specific blending properties on the CC3Material instance directly, and avoid making changes to this property.
Implemented in CC3MeshNode.
- (CC3Node *) parent [read, write, assign] |
The parent node of this node, in a node structural hierarchy.
This property is set automatically by the addChild: method. Usually, the application never needs to set this property directly.
- (int) podContentIndex [read, write, assign] |
The index of the POD data that forms the type-specific content of this node.
This is distinct from the podIndex property, which is the index of the data for the node, which may be of any node type. Once the type is established, the type-specific content is indexed by the podContentIndex property.
This abstract implementation does not map this property to an instance variable Concrete subclasses must override to map to an actual instance variable.
- (int) podParentIndex [read, write, assign] |
The index of the parent node of this node.
This will be -1 if this node has no parent.
This abstract implementation does not map this property to an instance variable Concrete subclasses must override to map to an actual instance variable.
- (CC3Vector) projectedLocation [read, write, assign] |
The current location of this node, as projected onto the 2D viewport coordinate space.
For most purposes, this is where this node will appear on the screen or window. The 2D position can be read from the X and Y components of the returned 3D location.
The initial value of this property is kCC3VectorZero. To set this property, pass this node as the argument to the projectNode: method of the active camera, which can be retrieved from the activeCamera property of the CC3World. The application should usually not set this property directly. For more information, see the notes for the projectNode: method of CC3Camera.
The Z-component of the returned location indicates the distance from the camera to this node, with a positive value indicating that this node is in front of the camera, and a negative value indicating that it is behind the camera. If you are only interested in the case when this node is in front of the camera (potentially visible to the camera), check that the Z-component of the returned location is positive.
When several nodes overlap a 2D position on the screen, you can also use the Z-component of the projectedLocation property of each of the nodes to determine which node is closest the camera, and is therefore "on-top" visually. This can be useful when trying to select a 3D node from an iOS touch event position.
The returned value takes into account the orientation of the device (portrait, landscape).
- (CGPoint) projectedPosition [read, assign] |
The current position of this node, as projected onto the 2D viewport coordinate space, returned as a 2D point.
For most purposes, this is where this node will appear on the screen or window.
This value is derived from the X and Y coordinates of the projectedLocation property. If this node is behind the camera, both the X and Y coordinates of the returned point will have the value -CGFLOAT_MAX.
The initial value of this property is CGPointZero. To set this property, pass this node as the argument to the projectNode: method of the active camera, which can be retrieved from the activeCamera property of the CC3World. For more information, see the notes for the projectNode: method of CC3Camera.
The returned value takes into account the orientation of the device (portrait, landscape).
- (CC3Vector4) quaternion [read, write, assign] |
The rotation of the node in 3D space, relative to the parent of this node, expressed as a quaternion.
Rotational transformation can also be specified as Euler angles using the rotation property. Subsequently, this quaternion property can then be read to return the corresponding quaternion.
- (CC3Vector) rotation [read, write, assign] |
The rotational orientation of the node in 3D space, relative to the parent of this node.
The global rotation of the node is therefore a combination of the global rotation of the parent of this node and the value of this rotation property. This value contains three Euler angles, defining a rotation of this nodearound the X, Y and Z axes. Each angle is specified in degrees.
Rotation is performed in Y-X-Z order, which is the OpenGL default. Depending on the nature of the object you are trying to control, you can think of this order as yaw, then pitch, then roll, or heading, then inclination, then tilt,
Rotational transformation can also be specified using the quaternion property. Subsequently, this rotation property can then be read to return the corresponding Euler angles.
- (CC3Vector) scale [read, write, assign] |
The scale of the node in each dimension, relative to the parent of this node.
- (BOOL) shouldCullBackFaces [read, write, assign] |
Indicates whether the back faces should be culled on the meshes contained in descendants of this node.
Setting this value sets the same property on all descendant nodes.
Querying this property returns NO if any of the descendant mesh nodes have this property set to NO. Initially, and in most cases, all mesh nodes have this property set to YES.
Be aware that culling improves performance, so this property should be set to NO only when specifically needed for visual effect, and only on the meshes that need it.
For more information about this use of this property, see the notes for the same property on the CC3MeshNode class, plus the class notes of that class.
Implemented in CC3MeshNode.
- (BOOL) shouldCullFrontFaces [read, write, assign] |
Indicates whether the front faces should be culled on the meshes contained in descendants of this node.
Setting this value sets the same property on all descendant nodes.
Querying this property returns YES if any of the descendant mesh nodes have this property set to YES. Initially, and in most cases, all mesh nodes have this property set to NO.
For more information about this use of this property, see the notes for the same property on the CC3MeshNode class, plus the class notes of that class.
Implemented in CC3MeshNode.
- (ccColor4F) specularColor [read, write, assign] |
The specular color of the materials of this node.
Setting this property sets the same property on all child nodes.
Querying this property returns the average value of querying this property on all child nodes. When querying this value on a large node assembly, be aware that this may be time-consuming.
Implemented in CC3Light, and CC3MeshNode.
- (CC3Node*) touchableNode [read, assign] |
Indicates the node that is of interest if this node is selected by a touch event.
The value of this property is not always this node, but may be an ancestor node instead.
This value of this property is this node if the isTouchEnabled property of this node is set to YES, or the nearest ancestor whose isTouchEnabled property is set to YES, or nil if neither this node, nor any ancestor has the isTouchEnabled property set to YES.
This design simplifies identifying the node that is of interest when a touch event occurs. Thus, a car may be drawn as a node assembly of many descendent nodes (doors, wheels, body, etc). If isTouchEnabled is set for the car structural node, but not each wheel, it will be the parent car node that will be returned by the touchableNode property of the car structural node, or each wheel node. This allows the user to touch a wheel, but still have the car identified as the object of interest.
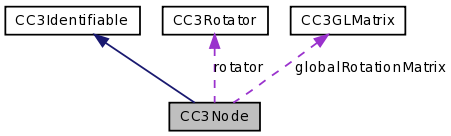
- (CC3GLMatrix *) transformMatrix [read, assign] |
The transformation matrix derived from the location, rotation and scale transform properties of this node and any ancestor nodes.
This matrix is recalculated automatically when the node is updated.
The transformation matrix for each node is global, in that it includes the transforms of all ancestors to the node. This streamlines rendering in that it allows the transform of each drawable node to be applied directly, and allows the order in which drawable nodes are drawn to be independent of the node structural hierarchy.
- (CC3GLMatrix *) transformMatrixInverted [read, assign] |
Returns the matrix inversion of the transformMatrix.
This can be useful for converting global transform properties, such as global location, rotation and scale to the local coordinate system of the node.
- (GLfloat) uniformScale [read, write, assign] |
The scale of the node, uniform in each dimension, relative to the parent of this node.
Unless non-uniform scaling is needed, it is preferable to use this property instead of the scale property.
If non-uniform scaling is applied via the scale property, this uniformScale property will return the length of the scale property vector divided by the length of a unit cube (sqrt(3.0)), as an approximation of the overall scaling condensed to a single scalar value.
- (BOOL) visible [read, write, assign] |
Controls whether this node shoud be displayed.
Initial value is YES.
You can set this to NO to make this node and all its descendants invisible to stop them from being displayed and to stop rendering processing on them.
When reading this property, the return value takes into consideration whether the parent is visible. As a result, setting this property to YES and then reading it may return NO if an ancestor has visibility set to NO.
The documentation for this class was generated from the following file:
 1.7.2
1.7.2