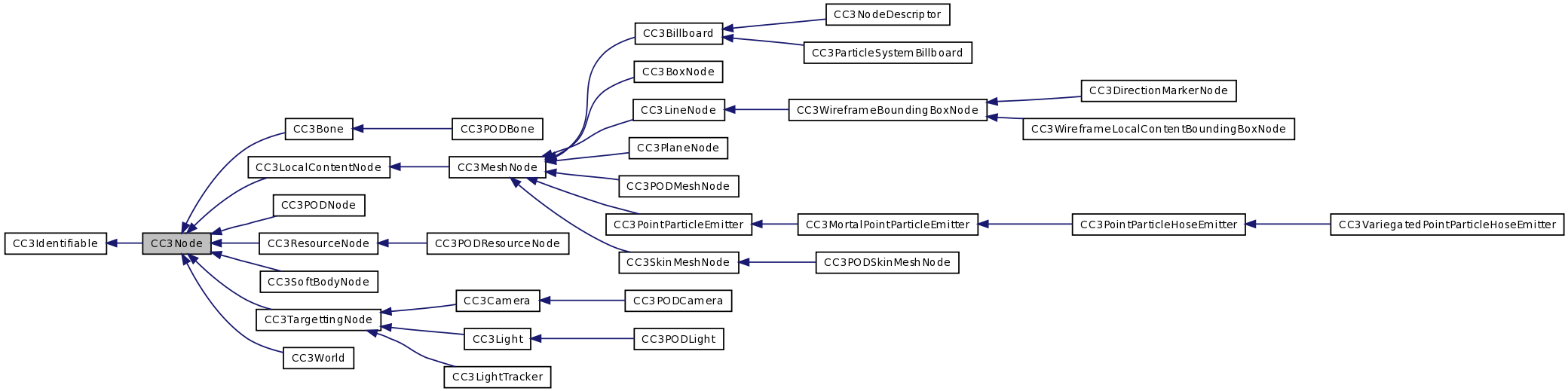
CC3Node and its subclasses form the basis of all 3D artifacts in the 3D world, including visible meshes, structures, cameras, lights, resources, and the 3D world itself. More...
#import <CC3Node.h>
Detailed Description
CC3Node and its subclasses form the basis of all 3D artifacts in the 3D world, including visible meshes, structures, cameras, lights, resources, and the 3D world itself.
Nodes can be moved, rotated and scaled. Rotation can be specified via either Euler angles or quaternions.
Nodes can be assembled in a structural hierarchy of parents and children, and transformations that are applied to a node are also applied to its descendant nodes. Typically, the root of a structural node hierarchy is an instance of CC3World.
Each node is automatically touched at two distinct times during animation frame handling. First, the updateBeforeTransform: and updateAfterTransform: methods are each invoked during scheduled model state updating, before and after the transformation matrix of the node is rebuilt, respectively. You should override udpateBeforeTransform: method to make any changes to the node, or its child nodes.
You should override updateAfterTransform: only if you need to make use of the global properties of the node or its child nodes, such as globalLocation, globalRotation, or globalScale. These properties are valid only after the transformMatrix has been calculated, and are therefore not valid within the updateBeforeTransform: method. However, if you make any changes to the transform properties (location, rotation, scale) of a node within the updateAfterTransform: method, you must invoke the updateTransformMatrices method on that node in order to have the changes applied to the node's transformMatrix.
Note that you do NOT need to invoke the updateTransformMatrices method for any changes made in the updateBeforeTransform: method, since those changes will automatically be applied to the transformMatrix.
The second place a node is touched is, the transformAndDrawWithVisitor: method, which is automaticaly invoked during each frame rendering cycle. You should have no need to override this method.
To maximize throughput, the operations of updating model state should be kept separate from the operations of frame rendering, and the two should not be mixed. Subclasses should respect this design pattern when overriding behaviour. Drawing operations should not be included in state updating, and vice versa. Since OpenGL is a hardware-accelerated state-machine pipeline, this separation allows frame-drawing operations to be performed by the GPU at the same time that state update operations for the next frame are being handled by the CPU, and on some systems, permits frame drawing and model updating to be perfomed on separate threads.
CC3Nodes support the cocos2d CCAction class hierarchy. Nodes can be translated, rotated, and scaled in three dimensions, or made to point towards a direction (for cameras and lights), all under control of cocos2d CCActions. As with other CCActions, these actions can be combined into action sequences or repeating actions, or modified with cocos2d ease actions. See the class CC3TransformTo and its subclasses for actions that operate on CC3Nodes.
When populating your world, you can easily create hordes of similar nodes using the copy and copyWithName: methods. Those methods effect deep copies to allow each copy to be manipulated independently, but will share underlying mesh data for efficient memory use. See the notes at the copy method for more details about copying nodes.
You can animate this class with animation data held in a subclass of CC3NodeAnimation. To animate this node using animation data, set the animation property to an instance of a subclass of the abstract CC3NodeAnimation class, populated with animation data, and then create an instance of a CC3Animate action, and run it on this node.
Nodes can respond to iOS touch events. The property isTouchEnabled can be set to YES to allow a node to be selected by a touch event. If the shouldInheritTouchability property is also set to YES, then this touchable capability can also be inherited from a parent node. Selection of nodes based on touch events is handled by CC3World. The nodeSelected:byTouchEvent:at: callback method of your customized CC3World will be invoked to indicate which node has been touched.
The iOS and PVR hardware expects textures to have width and height values that are a power-of-two (POT). If you are using textures that do not have POT dimensions, they will be converted to POT by the texture loader. If the corresponding mesh was not created in your 3D editor with this taken into consideration, you might find that the texture does not completely cover the mesh as expected. If this situation arises, you can compensate with the alignTextures and alignInvertedTextures methods to realign the texture coordinate arrays with the textures.
You can cause a wireframe box to be drawn around the node and all its descendants by setting the shouldDrawWireframeBox property to YES. This can be particularly useful during development to locate the boundaries of a node, or to locate a node that is not drawing properly. You can set the default color of this wireframe using the class-side defaultWireframeBoxColor property.
To maximize GL throughput, all OpenGL ES 1.1 state is tracked by the singleton instance [CC3OpenGLES11Engine engine]. CC3OpenGLES11Engine only sends state change calls to the GL engine if GL state really is changing. It is critical that all changes to GL state are made through the CC3OpenGLES11Engine singleton. When adding or overriding functionality in this framework, do NOT make gl* function calls directly if there is a corresponding state change tracker in the CC3OpenGLES11Engine singleton. Route the state change request through the CC3OpenGLES11Engine singleton instead.
Member Function Documentation
| - (void) addAndLocalizeChild: | (CC3Node *) | aNode |
Adds the specified node as a direct child node to this node, and localizes the child node's location, rotation, and scale properties to this node.
This has the effect of leaving the global location, rotation and scale of the child node as they were, but re-homing the node to this parent. Visually, the node appears to stay in place, but will now move with the new parent, not with the old parent.
For instance, you might have an apple object whose overall intended global size and orientation you know, but you want that object to be added to a bowl, so that when you move the bowl, the apple moves with it. The bowl has likely been rotated and scaled, and raised onto a table, and you don't want your known apple to be transformed by the table and bowl when you add the apple to the bowl, You can use this method on the bowl object to add the apple, and reverse the table and bowl transforms for the apple, so that the apple will appear with its current size and orientation.
To do this, this method finds the appropriate location, rotation, and scale properties for the child node that will result in the globalLocation, globalRotation and globalScale properties remaining the same after it has been added to this parent node.
The child node is removed from its existing parent.
This method makes use of the transformMatrices of this node and the node being added. To ensure that both matrices are each up to date, this method invokes updateTransformMatrix method on both this node and the node being added. You can therefore invoke this method without having to consider whether the transformMatrix has been calculated already.
This method changes the transform properties of the node being added. If you are invoking this method from the updateBeforeTransform: of the node being added, this node, or any ancestor node (including your CC3World), the transformMatrix of the node being added (and its descendant nodes) will automatically be updated. However, if you are invoking this method from the updateAfterTransform: method, you should invoke the updateTransformMatrices method on the node being added after this method is finished, to ensure that the transform matrices are udpated.
| - (void) addAxesDirectionMarkers |
Adds three visble direction marker lines, indicating the direction of the X, Y & Z axes, in the local coordinate system of this node.
The lines extend from the pivot location of this node (the origin in this node's local coordinate system) to a location somewhat outside the node in the direction of each of the X, Y & Z axes.
The lines are color-coded red, green and blue for the X, Y & Z axes, respectively, as an easy (RGB <=> XYZ) mnemonic.
See the addDirectionMarkerColored:inDirection: method for more info.
| - (void) addChild: | (CC3Node *) | aNode |
Adds the specified node as a direct child node to this node.
The child node is automatically removed from its existing parent.
It is safe to invoke this method more than once for the same child node. This method does nothing if the child already has this node as its parent.
If you are invoking this method from the updateBeforeTransform: of the node being added, this node, or any ancestor node (including your CC3World), the transformMatrix of the node being added (and its descendant nodes) will automatically be updated. However, if you are invoking this method from the updateAfterTransform: method, you should invoke the updateTransformMatrices method on the node being added after this method is finished, to ensure that the transform matrices are udpated.
| - (void) addDirectionMarker |
Adds a visble line, drawn in the color indicated by the directionMarkerColor class-side property, from the pivot location of this node (the origin in this node's local coordinate system) to a location somewhat outside the node in the direction kCC3VectorUnitZNegative, pointing down the negative Z-axis (which is the default direction in OpenGL).
For subclasses that use targetting, the line will point in the forwardDirection, which is the direction of the target location.
See the addDirectionMarkerColored:inDirection: method for more info.
| - (void) addDirectionMarkerColored: | (ccColor4F) | aColor | |
| inDirection: | (CC3Vector) | aDirection | |
Adds a visble line, drawn in the specified color, from the pivot location of this node (the origin in this node's local coordinate system) to a location somewhat outside the node in the specified direction.
The extent that the line will protrude from this node is proportional to the size of this node, as determined by the CC3DirectionMarkerNode class-side directionMarkerScale property.
The line is drawn by creating and adding a CC3DirectionMarkerNode as a child node to this node. The length of the child node is set from the boundingBox property of this node, so that the line protrudes somewhat from this node.
You can add more than one direction marker, and assign different colors to each.
This feature can be useful during development in helping to determine the rotational orientation of a 3D structural node.
By default, the child line node is not touchable, even if this node is touchable. If, for some reason you want the wireframe to be touchable, you can retrieve the direction marker nodes via the directionMarkers property, and set the isTouchEnabled property to YES.
| - (void) alignInvertedTextures |
Aligns the texture coordinates held by a mesh in any descendant node with the textures held in the material of that mesh node.
The texture coordinates are aligned assuming that the texture is inverted in the Y-direction. Certain texture formats are inverted during loading, and this method can be used to compensate.
This method can be useful when the width and height of the textures in the material are not a power-of-two. Under iOS, when loading a texture that is not a power-of-two, the texture will be converted to a size whose width and height are a power-of-two. The result is a texture that can have empty space on the top and right sides. If the texture coordinates of the mesh do not take this into consideration, the result will be that only the lower left of the mesh will be covered by the texture.
When this occurs, invoking this method will adjust the texture coordinates of the mesh to map to the original width and height of the texturesa.
If the mesh is using multi-texturing, this method will adjust the texture coordinates array for each texture unit, using the corresponding texture for that texture unit in the specified material.
Care should be taken when using this method, as it affects all descendant nodes, and changes the actual vertex data. This method should only be invoked once on any mesh, and it may cause mapping conflicts if the same mesh is shared by other nodes that use different textures.
To adjust the texture coordinates of only a single mesh, invoke this method on that mesh node only, or invoke the alignWithInvertedTexturesIn: in the CC3Mesh within that mesh node. To adjust the texture coordinates of only a single texture coordinates array within a mesh, invoke the alignWithInvertedTexture: method on the appropriate instance of CC3VertexTextureCoordinates.
Implemented in CC3MeshNode.
| - (void) alignTextures |
Aligns the texture coordinates held by a mesh in any descendant node with the textures held in the material of that mesh node.
This method can be useful when the width and height of the textures in the material are not a power-of-two. Under iOS, when loading a texture that is not a power-of-two, the texture will be converted to a size whose width and height are a power-of-two. The result is a texture that can have empty space on the top and right sides. If the texture coordinates of the mesh do not take this into consideration, the result will be that only the lower left of the mesh will be covered by the texture.
When this occurs, invoking this method will adjust the texture coordinates of the mesh to map to the original width and height of the textures.
If the mesh is using multi-texturing, this method will adjust the texture coordinates array for each texture unit, using the corresponding texture for that texture unit in the specified material.
Care should be taken when using this method, as it changes the actual vertex data. This method should only be invoked once on any mesh, and it may cause mapping conflicts if the same mesh is shared by other CC3MeshNodes that use different textures.
Care should be taken when using this method, as it affects all descendant nodes, and changes the actual vertex data. This method should only be invoked once on any mesh, and it may cause mapping conflicts if the same mesh is shared by other nodes that use different textures.
To adjust the texture coordinates of only a single mesh, invoke this method on that mesh node only, or invoke the alignWithTexturesIn: in the CC3Mesh within that mesh node. To adjust the texture coordinates of only a single texture coordinates array within a mesh, invoke the alignWithTexture: method on the appropriate instance of CC3VertexTextureCoordinates.
Implemented in CC3MeshNode.
| - (NSString*) appendStructureDescriptionTo: | (NSMutableString *) | desc | |
| withIndent: | (NSUInteger) | indentLevel | |
Appends the description of this node to the specified mutable string, on a new line and indented the specified number of levels.
Returns the specified mutable string, as a convenience.
| - (CC3TargettingNode*) asCameraTracker |
Wraps this node in an instance of CC3TargettingNode, and returns the autoreleased CC3TargettingNode instance.
This node appears as the lone child node of the returned targetting node.
Both the shouldTrackTarget and shouldAutotargetCamera properties of the returned targetting node are set to YES, indicating that the targetting node will automatically find the camera and always face it.
The shouldAutoremoveWhenEmpty property of the returned targetting node is set to YES, indicating that the targetting node will remove itself automatically from the node hierarchy when the last child node (likely this node) is removed from the targetting node. This assists in cleaning up nodes in the hierarchy by avoiding leaving empty wrapper nodes littering the hierarchy.
The CC3TargettingNode instance will have the name "<this node name>-TargettingWrapper".
| - (CC3TargettingNode*) asLightTracker |
Wraps this node in an instance of CC3LightTracker, and returns the autoreleased CC3LightTracker instance.
This node appears as the lone child node of the returned light tracker node.
The shouldTrackTarget property of the returned light tracker is set to YES, indicating and the tracker will always face whatever node is subsequently set in the target property.
The shouldAutoremoveWhenEmpty property of the returned targetting node is set to YES, indicating that the targetting node will remove itself automatically from the node hierarchy when the last child node (likely this node) is removed from the targetting node. This assists in cleaning up nodes in the hierarchy by avoiding leaving empty wrapper nodes littering the hierarchy.
The CC3LightTracker instance will have the name "<this node name>-LightTrackerWrapper".
| - (CC3TargettingNode*) asTargettingNode |
Wraps this node in an instance of CC3TargettingNode, and returns the autoreleased CC3TargettingNode instance.
This node appears as the lone child node of the returned targetting node.
The CC3TargettingNode instance will have the name "<this node name>-TargettingWrapper".
| - (CC3TargettingNode*) asTracker |
Wraps this node in an instance of CC3TargettingNode, and returns the autoreleased CC3TargettingNode instance.
This node appears as the lone child node of the returned targetting node.
The shouldTrackTarget property of the returned targetting node is set to YES, indicating and the targetting node will always face whatever node is subsequently set in the target property.
The shouldAutoremoveWhenEmpty property of the returned targetting node is set to YES, indicating that the targetting node will remove itself automatically from the node hierarchy when the last child node (likely this node) is removed from the targetting node. This assists in cleaning up nodes in the hierarchy by avoiding leaving empty wrapper nodes littering the hierarchy.
The CC3TargettingNode instance will have the name "<this node name>-TargettingWrapper".
| - (void) bindRestPose |
Binds the rest pose of any skeletons contained within the descendants of this node.
This method must be invoked once the initial locations and rotations of each bone in the skeletons are set.
These initial bone orientations are those that align with the native structure of the vertices in the mesh, and collectively are known as the rest pose of the skeleton. Changes to the transform properties of the individual bone nodes, relative to the rest pose, will deform the mesh from its natural structure.
The bone transforms must be calculated locally from the perspective of the CC3SoftBodyNode that contains a skeleton and skin mesh. This method should only be invoked on the CC3SoftBodyNode or a structural ancestor of that node,
This implementation simply passes this invocation along to the children of this node. Subclasses contained in the soft-body node will add additional functionality.
| - (void) buildTransformMatrixWithVisitor: | (CC3NodeTransformingVisitor *) | visitor |
Template method that recalculates the transform matrix of this node from the location, rotation and scale transformation properties, using the specified visitor.
This method is invoked automatically by the visitor. Usually the application never needs to invoke this method.
| - (void) checkDrawingOrder |
Checks that the child nodes of this node are in the correct drawing order relative to other nodes.
This implementation forwards this request to all descendants. Those descendants with local content to draw will check their positions in the drawing sequence by passing this notification up the ancestor chain to the CC3World.
By default, nodes are automatically repositioned on each drawing frame to optimize the drawing order, so you should usually have no need to use this method.
However, in order to eliminate the overhead of checking each node during each drawing frame, you can disable this automatic behaviour by setting the allowSequenceUpdates property of specific drawing sequencers to NO.
In that case, if you modify the properties of a node or its content, such as mesh or material opacity, and your CC3World drawing sequencer uses that criteria to sort nodes, you can invoke this method to force the node to be repositioned in the correct drawing order.
You don't need to invoke this method when initially setting the properties. You only need to invoke this method if you modify the properties after the node has been added to the CC3World, either by itself, or as part of a node assembly.
Implemented in CC3LocalContentNode.
| - (void) cleanup |
Stops all running CCActions for this node and all descendant nodes.
Effectively invokes stopAllActions on this node and all descendant nodes.
| - (id) copy |
Returns a newly allocated (retained) copy of this instance.
The new copy will have the same name as this node, but will have a unique tag.
The copying operation effects a deep copy. For any content that is held by reference (eg- objects), and subject to future modification, a copy is created, so that both this instance and the other instance can be treated independently. This includes child nodes, of which copies are created.
The following rules are applied when copying a node:
- The tag property is not copied. The tag is property is assigned and automatically generated unique tag value.
- The copy will initially have no parent. It will automatically be set when this node is added as a child to a parent node.
- Copies are created of all child nodes, using the copy method of each child. The child nodes of the new node will therefore have the same names as the child nodes of the original node.
- Mesh data is copied by reference, not by value. Child nodes that support mesh data will assign it by reference when that child is copied. Mesh data is shared between both the original mesh node and copy node.
Subclasses that extend content should honour the deep copy design pattern, making exceptions only for content that is both large and not subject to modifications, such as mesh data.
This method may often be used to duplicate a node many times, to create large number of similar instances to populate a game. To help you verify that you are correctly releasing and deallocating all these copies, you can use the instanceCount class method to get a current count of the total number of instances of all subclasses of CC3Identifiable, When reviewing that number, remember that nodes are only one type of CC3Identifiable, and other subclasses, such as materials, will contribute to this count.
Implements CC3Identifiable.
| - (id) copyWithName: | (NSString *) | aName |
Returns a newly allocated (retained) copy of this instance.
The new copy will have its name set to the specified name, and will have a unique tag.
The copying operation effects a deep copy. See the notes at the copy method for more details about copying nodes.
Implements CC3Identifiable.
| - (void) createGLBuffers |
Creates OpenGL ES buffers to be used by the GL engine hardware.
Default behaviour is to invoke the same method on all child nodes. Subclasses that can make use of hardware buffering, notably mesh subclasses, will override and bind their data to GL hardware buffers.
Invoking this method is optional and is not performed automatically. If an application does not wish to use hardware buffering for some nodes, it can do so by avoiding the invocation of this method on those nodes. Typically, however, an applicaiton will simply invoke this method once during initialization of highest-level ancestor node (ususally a subclass of CC3World).
| + (GLfloat) defaultScaleTolerance |
The default value used to set the initial value of the scaleTolerance property of new CC3Node instances.
The initial value of this property is zero, indicating that no tolerance is accepted. Each scaling component will only be considered to be unity if it is exactly equal to one, and scaling will only be considered to be uniform if all three components are exactly equal to each other.
| - (void) deleteGLBuffers |
Deletes any OpenGL buffers that were created by any child nodes via a prior invocation of createGLBuffers.
If the child nodes also retained the data locally, drawing will then revert to distinct GL draw calls, passing data through the GL API on each call, rather than via the bound buffers.
| + (CGFloat) descriptorFontSize |
Returns the font size that will be used when drawing the descriptor text when the shouldDrawDescriptor property is set to YES on any node.
The initial value of this class-side property is 14.0.
| + (ccColor4F) directionMarkerColor |
Returns the color that direction marker lines will be drawn in when created using the addDirectionMarker method.
Setting this property to kCCC4FBlackTransparent will cause the color of any new direction marker lines to be set to the value of the color property of the node instead.
The initial value of this class property is kCCC4FRed.
| - (void) disableAllAnimation |
Disables animation of this node, and all descendant nodes, from animation data held in the animation property of this node and each descendant node.
| - (void) disableAnimation |
Disables animation of this node from animation data held in the animation property.
This will not disable animation of child nodes.
| - (BOOL) doesIntersectFrustum: | (CC3Frustum *) | aFrustum |
Returns whether the local content of this node intersects the given frustum.
This check does not include checking children, only the local content.
This method is called during the drawing operations of each frame to determine whether this node should be culled from the visible nodes and not drawn. A return value of YES will cause the node to be drawn, a return value of NO will cause the node to be culled and not drawn.
Culling nodes that are not visible to the camera is an important performance enhancement. The node should strive to be as accurate as possible in returning whether it intersects the camera's frustum. Incorrectly returning YES will cause wasted processing within the GL engine. Incorrectly returning NO will cause a node that should at least be partially visible to not be drawn.
In this implementation, if this node has a boundingVolume, this method delegates to it. Otherwise, it simply returns YES. Subclasses may override to change this standard behaviour.
| - (void) doNotBufferVertexColors |
Convenience method to cause the vertex color data of this node and all descendant nodes to be skipped when createGLBuffers is invoked.
The vertex data is not buffered to a a GL VBO, is retained in application memory, and is submitted to the GL engine on each frame render.
Only the vertex colors will not be buffered to a GL VBO. Any other vertex data, such as locations, or texture coordinates, will be buffered to a GL VBO when createGLBuffers is invoked.
This method causes the vertex data to be retained in application memory, so, if you have invoked this method, you do NOT also need to invoke the retainVertexColors method.
| - (void) doNotBufferVertexIndices |
Convenience method to cause the vertex index data of this node and all descendant nodes to be skipped when createGLBuffers is invoked.
The vertex data is not buffered to a a GL VBO, is retained in application memory, and is submitted to the GL engine on each frame render.
Only the vertex indices will not be buffered to a GL VBO. Any other vertex data, such as locations, or texture coordinates, will be buffered to a GL VBO when createGLBuffers is invoked.
This method causes the vertex data to be retained in application memory, so, if you have invoked this method, you do NOT also need to invoke the retainVertexColors method.
| - (void) doNotBufferVertexLocations |
Convenience method to cause the vertex location data of this node and all descendant nodes to be skipped when createGLBuffers is invoked.
The vertex data is not buffered to a a GL VBO, is retained in application memory, and is submitted to the GL engine on each frame render.
Only the vertex locations will not be buffered to a GL VBO. Any other vertex data, such as normals, or texture coordinates, will be buffered to a GL VBO when createGLBuffers is invoked.
This method causes the vertex data to be retained in application memory, so, if you have invoked this method, you do NOT also need to invoke the retainVertexLocations method.
| - (void) doNotBufferVertexNormals |
Convenience method to cause the vertex normal data of this node and all descendant nodes to be skipped when createGLBuffers is invoked.
The vertex data is not buffered to a a GL VBO, is retained in application memory, and is submitted to the GL engine on each frame render.
Only the vertex normals will not be buffered to a GL VBO. Any other vertex data, such as locations, or texture coordinates, will be buffered to a GL VBO when createGLBuffers is invoked.
This method causes the vertex data to be retained in application memory, so, if you have invoked this method, you do NOT also need to invoke the retainVertexNormals method.
| - (void) doNotBufferVertexTextureCoordinates |
Convenience method to cause the vertex texture coordinate data of this node and all descendant nodes, for all texture units used by those nodes, to be skipped when createGLBuffers is invoked.
The vertex data is not buffered to a a GL VBO, is retained in application memory, and is submitted to the GL engine on each frame render.
Only the vertex texture coordinates will not be buffered to a GL VBO. Any other vertex data, such as locations, or texture coordinates, will be buffered to a GL VBO when createGLBuffers is invoked.
This method causes the vertex data to be retained in application memory, so, if you have invoked this method, you do NOT also need to invoke the retainVertexTextureCoordinates method.
| - (void) drawWithVisitor: | (CC3NodeDrawingVisitor *) | visitor |
Draws the content of this node to the GL engine.
The specified visitor encapsulates the frustum of the currently active camera, and certain drawing options.
As described in the class documentation, in keeping with best practices, drawing and frame rendering should be kept separate from updating the model state. Therefore, when overriding this method in a subclass (or any of the template methods invoked by this method), do not update any model state. This method should perform only frame rendering operations.
This method is invoked automatically as part of the drawing operations initiated by the transformAndDrawWithVisitor: method.
Implemented in CC3MeshNode.
| - (void) enableAllAnimation |
Enables animation of this node, and all descendant nodes, from animation data held in the animation property of this node and each descendant node.
| - (void) enableAnimation |
Enables animation of this node from animation data held in the animation property.
This will not enable animation of child nodes.
| - (void) establishAnimationFrameAt: | (ccTime) | t |
Updates the location, rotation and scale of this node based on the animation frame located at the specified time, which should be a value between zero and one, with zero indicating the first animation frame, and one indicating the last animation frame.
Only those properties of this node for which there is animation data will be changed.
This implementation delegates to the CC3NodeAnimation instance held in the animation property, then passes this notification along to child nodes to align them with the same animation frame. Linear interpolation of the frame data may be performed, based on the number of frames and the specified time.
If disableAnimation or disableAllAnimation has been invoked on this node, it will be excluded from animation, and this method will not have any affect on this node. However, this method will be propagated to child nodes.
This method is invoked automatically from an instance of CC3Animate that is animating this node. Usually, the application never needs to invoke this method directly.
| - (CCArray*) flatten |
Returns an autoreleased array containing this node and all its descendants.
This is done by invoking flattenInto: with a newly-created array, and returning the array.
| - (void) flattenInto: | (CCArray *) | anArray |
Adds this node to the specified array, and then invokes this method on each child node.
The effect is to populate the array with this node and all its descendants.
| - (CCAction*) getActionByTag: | (int) | tag |
Gets an action from the running action list given its tag.
| - (CC3Node*) getNodeNamed: | (NSString *) | aName |
Retrieves the first node found with the specified name, anywhere in the structural hierarchy of descendants of this node (not just direct children).
The hierarchy search is depth-first.
| - (CC3Node*) getNodeTagged: | (GLuint) | aTag |
Retrieves the first node found with the specified tag, anywhere in the structural hierarchy of descendants of this node (not just direct children).
The hierarchy search is depth-first.
| - (BOOL) isDescendantOf: | (CC3Node *) | aNode |
Returns whether this node is a structural descendant (child, grandchild, etc) of the specified node.
| - (void) linkToPODNodes: | (CCArray *) | nodeArray |
Create links to the nodes in the specified array.
This implementation attaches this node to its parent as identified by the podParentIndex property. Subclasses may override to perform other linking.
| - (void) markTransformDirty |
Indicates that the transformation matrix is dirty and needs to be recalculated.
This method is invoked automatically as needed. Usually the application never needs to invoke this method directly.
| + (id) node |
Allocates and initializes an autoreleased unnamed instance with an automatically generated unique tag value.
The tag value is generated using a call to nextTag.
| + (id) nodeAtIndex: | (int) | aPODIndex | |
| fromPODResource: | (CC3PODResource *) | aPODRez | |
Allocates and initializes an autoreleased instance from the data of this type at the specified index within the specified POD resource.
| - (PODStructPtr) nodePODStructAtIndex: | (uint) | aPODIndex | |
| fromPODResource: | (CC3PODResource *) | aPODRez | |
Returns the underlying SPODNode data structure from the specified resource, for the SPODNode at the specified index.
The returned pointer must be cast to SPODNode before accessing any internals of the data structure.
| + (id) nodeWithName: | (NSString *) | aName |
Allocates and initializes an autoreleased instance with the specified name and an automatically generated unique tag value.
The tag value is generated using a call to nextTag.
| + (id) nodeWithTag: | (GLuint) | aTag |
Allocates and initializes an unnamed autoreleased instance with the specified tag.
| + (id) nodeWithTag: | (GLuint) | aTag | |
| withName: | (NSString *) | aName | |
Allocates and initializes an autoreleased instance with the specified tag and name.
| - (int) numberOfRunningActions |
Returns the numbers of actions that are running plus the ones that are scheduled to run (actions in actionsToAdd and actions arrays).
Composable actions are counted as 1 action. Example: If you are running 1 Sequence of 7 actions, it will return 1. If you are running 7 Sequences of 2 actions, it will return 7.
| - (void) reattachBonesFrom: | (CC3Node *) | aNode |
After copying a skin mesh node, the newly created copy will still be influenced by the original skeleton.
The result is that both the original mesh and the copy will move and be deformed in tandem as the skeleton moves.
If you are creating a chorus line of dancing characters, this may be the effect you are after. However, if you are creating a squadron of similar, but independently moving characters, each skin mesh node copy should be controlled by a separate skeleton.
After creating a copy of the skeleton bone node assembly, you can use this method to attach the skin mesh node to the new skeleton. The node that is provided as the argument to this method is the root bone node of the skeleton, or a structural ancestor of the skeleton that does not also include the original skeleton as a descendant.
This method iterates through all the bones referenced by any descendant skin mesh nodes, and retrieves a bone with the same name from the structural descendants of the specified node.
When copying a CC3SoftBodyNode instance, this method is automatically invoked as part of the copying of the soft-body object, and you do not need to invoke this method directly.
| - (void) rebuildBoundingVolume |
If the shouldUseFixedBoundingVolume property is set to NO, this method forces the bounding volume to be rebuilt.
Otherwise, this method does nothing.
If this node has an underlying mesh, and you have changed the vertex locations in the mesh, you should invoke this method to ensure that the bounding volume is rebuilt to encompass the new vertex locations.
The bounding volume is automatically transformed as the node is transformed, so this method does NOT need to be invoked when the node is transformed (moved, rotated, or scaled).
| - (void) releaseRedundantData |
Once the elements data has been buffered into a GL vertex buffer object (VBO) within the GL engine, via the createGLBuffer method, this method can be used to release the data in main memory that is now redundant from all meshes that have been buffered to the GL engine.
Invoking this method on a node will release from main memory any data within all descendant mesh nodes, that has successfully been copied to buffers in the GL engine. It is safe to invokde this method even if createGLBuffer has not been invoked, and even if VBO buffering was unsuccessful.
To exempt vertex data from release, invoke one or more of the following methods once on nodes for which data should be retained, before invoking this method:
- retainVertexLocations
- retainVertexNormals
- retainVertexColors
- retainVertexTextureCoordinates
- retainVertexIndices
For example, sophisticated physics engines and collision detection algorithms may make use of vertex location data in main memory. Or a rippling texture animation might retain texture coordinate data in order to dyamically adjust the texture coordinate data.
Normally, you would invoke the retainVertex... methods on specific individual nodes, and then invoke this method on the parent node of a node assembly, or on the CC3World.
| - (void) remove |
Convenience method that removes this node from its structural hierarchy by simply invoking removeChild: on the parent of this node.
If the shouldCleanupWhenRemoved property of this node is set to YES, any CCActions running on this node will be stopped and removed. If the shouldCleanupWhenRemoved property of this node is set to NO, any CCActions running on that node will be paused, but not removed.
Stopping and removing CCActions is important because the actions running on a node retain links to the node. If the actions are simply paused, those links will be retained forever, potentially creating memory leaks of nodes that are invisibly retained by their actions.
By default, the shouldCleanupWhenRemoved property is set to YES, and all CCActions running on this node will be stopped and removed. If the shouldCleanupWhenRemoved is set to NO, it is up to you to clean up any running CCActions when you are done with this node. You can do this using either the stopAllActions or cleahup method.
During a node visitation run with a CCNodeVisitor, you should avoid using this method directly. The visitation process involves iterating through collections of child nodes, and removing a node during the iteration of a collection raises an error.
Instead, during a visitation run, you can use the requestRemovalOf: method on the visitor, which safely processes all removal requests once the full visitation run is complete.
| - (void) removeAllChildren |
Removes all child nodes of this node.
| - (void) removeAllDirectionMarkers |
Removes all the direction marker child nodes that were previously added using the addDirectionMarkerColored:inDirection: and addDirectionMarker methods.
| - (void) removeChild: | (CC3Node *) | aNode |
Removes the specified node as a direct child node to this node.
Does nothing if the specified node is not actually a child of this node.
If the shouldCleanupWhenRemoved property of the node being removed is set to YES, any CCActions running on that node will be stopped and removed. If the shouldCleanupWhenRemoved property of the node being removed is set to NO, any CCActions running on that node will be paused, but not removed.
Stopping and removing CCActions is important because the actions running on a node retain links to the node. If the actions are simply paused, those links will be retained forever, potentially creating memory leaks of nodes that are invisibly retained by their actions.
By default, the shouldCleanupWhenRemoved property is set to YES, and all CCActions running on the node being removed will be stopped and removed. If the shouldCleanupWhenRemoved is set to NO, it is up to you to clean up any running CCActions when you are done with the node. You can do this using either the stopAllActions or cleahup method.
If the shouldAutoremoveWhenEmpty property is YES, and the last child node is being removed, this node will invoke its own remove method to remove itself from the node hierarchy as well. See the notes for the shouldAutoremoveWhenEmpty property for more info on autoremoving when all child nodes have been removed.
| - (void) retainVertexColors |
Convenience method to cause the vertex color data of this node and all descendant nodes to be retained in application memory when releaseRedundantData is invoked, even if it has been buffered to a GL VBO.
Use this method if you require access to vertex data after the data has been buffered to a GL VBO.
Only the vertex colors will be retained. Any other vertex data, such as locations, or texture coordinates, that has been buffered to GL VBO's, will be released from application memory when releaseRedundantData is invoked.
| - (void) retainVertexIndices |
Convenience method to cause the vertex index data of this node and all descendant nodes to be retained in application memory when releaseRedundantData is invoked, even if it has been buffered to a GL VBO.
Use this method if you require access to vertex data after the data has been buffered to a GL VBO.
Only the vertex indices will be retained. Any other vertex data, such as locations, or texture coordinates, that has been buffered to GL VBO's, will be released from application memory when releaseRedundantData is invoked.
| - (void) retainVertexLocations |
Convenience method to cause the vertex location data of this node and all descendant nodes to be retained in application memory when releaseRedundantData is invoked, even if it has been buffered to a GL VBO.
Use this method if you require access to vertex data after the data has been buffered to a GL VBO.
Only the vertex locations will be retained. Any other vertex data, such as normals, or texture coordinates, that has been buffered to GL VBO's, will be released from application memory when releaseRedundantData is invoked.
| - (void) retainVertexNormals |
Convenience method to cause the vertex normal data of this node and all descendant nodes to be retained in application memory when releaseRedundantData is invoked, even if it has been buffered to a GL VBO.
Use this method if you require access to vertex data after the data has been buffered to a GL VBO.
Only the vertex normals will be retained. Any other vertex data, such as locations, or texture coordinates, that has been buffered to GL VBO's, will be released from application memory when releaseRedundantData is invoked.
| - (void) retainVertexTextureCoordinates |
Convenience method to cause the vertex texture coordinate data of this node and all descendant nodes, for all texture units, used by this mesh to be retained in application memory when releaseRedundantData is invoked, even if it has been buffered to a GL VBO.
Use this method if you require access to vertex data after the data has been buffered to a GL VBO.
Only the vertex texture coordinates will be retained. Any other vertex data, such as locations, or normals, that has been buffered to GL VBO's, will be released from application memory when releaseRedundantData is invoked.
| - (void) rotateBy: | (CC3Vector) | aRotation |
Rotates this node from its current rotational state by the specified Euler angles in degrees.
The incoming Euler angles specify the amount of change in rotation, not the final rotational state.
| - (void) rotateByAngle: | (GLfloat) | anAngle | |
| aroundAxis: | (CC3Vector) | anAxis | |
Rotates this node from its current rotational state by rotating around the specified axis by the specified angle in degrees.
The incoming axis and angle specify the amount of change in rotation, not the final rotational state.
Thanks to cocos3d user nt901 for contributing to the development of this feature
| - (void) rotateByQuaternion: | (CC3Vector4) | aQuaternion |
Rotates this node from its current rotational state by the specified quaternion.
The incoming quaternion specifies the amount of change in rotation, not the final rotational state.
| - (CCAction*) runAction: | (CCAction *) | action |
Executes an action, and returns the action that is executed.
The node becomes the action's target.
| + (void) setDefaultScaleTolerance: | (GLfloat) | aTolerance |
Sets the default value used to set the initial value of the property of new CC3Node instances.
The initial value of this property is zero, indicating that no tolerance is accepted. Each scaling component will only be considered to be unity if it is exactly equal to one, and scaling will only be considered to be uniform if all three components are exactly equal to each other.
| + (void) setDescriptorFontSize: | (CGFloat) | fontSize |
Sets the font size that will be used when drawing the descriptor text when the shouldDrawDescriptor property is set to YES on any node.
The initial value of this class-side property is 14.0.
| + (void) setDirectionMarkerColor: | (ccColor4F) | aColor |
Sets the color that direction marker lines will be drawn in when created using the addDirectionMarker method.
Changing this property will affect the color of any new direction marker lines created. It does not affect any existing direction marker lines.
Setting this property to kCCC4FBlackTransparent will cause the color of any new direction marker lines to be set to the value of the color property of the node instead.
The initial value of this class property is kCCC4FRed.
| + (void) setWireframeBoxColor: | (ccColor4F) | aColor |
Sets the color that wireframes will be drawn in when created using the shouldDrawWireframeBox property.
Changing this property will affect the color of any new wireframe bounding boxes created. It does not affect any instances that already have a wireframe bounding box established.
Setting this property to kCCC4FBlackTransparent will cause the color of any new wireframe bounding boxes to be set to the value of the color property of the node instead.
The initial value of this class property is kCCC4FYellow.
| - (void) stopAction: | (CCAction *) | action |
Removes an action from the running action list.
| - (void) stopActionByTag: | (int) | tag |
Removes an action from the running action list given its tag.
| - (void) stopAllActions |
Removes all actions from the running action list.
| - (void) touchDisableAll |
Sets the isTouchEnabled property to NO on this node and all descendant nodes.
This is a convenience method that will make this node and all its decendants unresponsive to touches. For more info see the notes for the isTouchEnabled and touchableNode properties.
| - (void) touchEnableAll |
Sets the isTouchEnabled property to YES on this node and all descendant nodes.
This is a convenience method that will make all descendants individually touchable and selectable, which is not usually what is wanted. Usually, you would set isTouchEnabled on specific parent nodes that are of interest to select a sub-assembly as a whole. However, making all components individually selectable can sometimes be desired, and is useful for testing.
For more info see the notes for the isTouchEnabled and touchableNode properties.
This is a convenience method that can find use in testing, where it might be of interest to be able to individually select small components of a larger assembly.
| - (void) transformAndDrawWithVisitor: | (CC3NodeDrawingVisitor *) | visitor |
Template method that applies this node's transform matrix to the GL matrix stack and draws this node using the specified visitor.
This method is invoked by the drawing visitor when it visits the node, if all of the following conditions are met by this node:
- ths node is visible (as indicated by the visible property)
- has content to draw (as indicated by the hasLocalContent property)
- intersects the camera's frustum (which is checked by invoking the method doesIntersectFrustum: of this node with the frustum from the visitor).
If all of these tests pass, drawing is required, and this method transforms and draws the local content of this node.
This method is automatically invoked from the visitor. The application should never have need to used this method.
| - (id) transformVisitorClass |
Returns the class of visitor that will automatically be instantiated when visiting this node to transform, without updating.
The returned class must be a subclass of CC3NodeTransformingVisitor. This implementation returns CC3NodeTransformingVisitor. Subclasses may override to customize the behaviour of the updating visits.
| - (void) translateBy: | (CC3Vector) | aVector |
Translates the location of this node by the specified vector.
The incoming vector specify the amount of change in location, not the final location.
| - (void) updateAfterTransform: | (CC3NodeUpdatingVisitor *) | visitor |
This template method is invoked periodically whenever the 3D nodes are to be updated.
This method provides this node with an opportunity to perform update activities after the transformMatrix of the node has been recalculated. The similar and complimentary method updateBeforeTransform: is automatically invoked before the transformMatrix has been recalculated.
The global transform properties of a node (globalLocation, globalRotation, globalScale) will have accurate values when this method is run, since they are only valid after the transformMatrix has been updated. If you need to make use of the global properties of a node (such as for collision detection), override this method.
Since the transformMatrix has already been updated when this method is invoked, if you override this method and make any changes to the transform properties (location, rotation, scale) of any node, you should invoke the updateTransformMatrices method of that node, to have its transformMatrix, and those of its child nodes, recalculated.
This abstract template implementation does nothing. Subclasses that need access to their global transform properties will override accordingly. Subclasses that override do not need to invoke this superclass implementation. Nor do subclasses need to invoke this method on their child nodes. That is performed automatically.
The specified visitor encapsulates the CC3World instance, to allow this node to interact with other nodes in its world.
The visitor also encapsulates the deltaTime, which is the interval, in seconds, since the previous update. This value can be used to create realistic real-time motion that is independent of specific frame or update rates. Depending on the setting of the maxUpdateInterval property of the CC3World instance, the value of dt may be clamped to an upper limit before being passed to this method. See the description of the CC3World maxUpdateInterval property for more information about clamping the update interval.
If you wish to remove this node during an update visitation, avoid invoking the remove method on the node from this method. The visitation process involves iterating through collections of child nodes, and removing a node during the iteration of a collection raises an error. Instead, you can use the requestRemovalOf: method on the visitor, which safely processes all removal requests once the full visitation run is complete.
As described in the class documentation, in keeping with best practices, updating the model state should be kept separate from frame rendering. Therefore, when overriding this method in a subclass, do not perform any drawing or rending operations. This method should perform model updates only.
This method is invoked automatically at each scheduled update. Usually, the application never needs to invoke this method directly.
| - (void) updateBeforeTransform: | (CC3NodeUpdatingVisitor *) | visitor |
This template method is invoked periodically whenever the 3D nodes are to be updated.
This method provides this node with an opportunity to perform update activities before any changes are applied to the transformMatrix of the node. The similar and complimentary method updateAfterTransform: is automatically invoked after the transformMatrix has been recalculated. If you need to make changes to the transform properties (location, rotation, scale) of the node, or any child nodes, you should override this method to perform those changes.
The global transform properties of a node (globalLocation, globalRotation, globalScale) will not have accurate values when this method is run, since they are only valid after the transformMatrix has been updated. If you need to make use of the global properties of a node (such as for collision detection), override the udpateAfterTransform: method instead, and access those properties there.
This abstract template implementation does nothing. Subclasses that act predictively, such as those undergoing trajectories or IPO curves can update their properties accordingly. Subclasses that override do not need to invoke this superclass implementation. Nor do subclasses need to invoke this method on their child nodes. That is performed automatically.
The specified visitor encapsulates the CC3World instance, to allow this node to interact with other nodes in its world.
The visitor also encapsulates the deltaTime, which is the interval, in seconds, since the previous update. This value can be used to create realistic real-time motion that is independent of specific frame or update rates. Depending on the setting of the maxUpdateInterval property of the CC3World instance, the value of dt may be clamped to an upper limit before being passed to this method. See the description of the CC3World maxUpdateInterval property for more information about clamping the update interval.
If you wish to remove this node during an update visitation, avoid invoking the remove method on the node from this method. The visitation process involves iterating through collections of child nodes, and removing a node during the iteration of a collection raises an error. Instead, you can use the requestRemovalOf: method on the visitor, which safely processes all removal requests once the full visitation run is complete.
As described in the class documentation, in keeping with best practices, updating the model state should be kept separate from frame rendering. Therefore, when overriding this method in a subclass, do not perform any drawing or rending operations. This method should perform model updates only.
This method is invoked automatically at each scheduled update. Usually, the application never needs to invoke this method directly.
| - (void) updateTransformMatrices |
Applies the transform properties (location, rotation, scale) to the transformMatrix of this node, and all descendant nodes.
To ensure that the transforms are accurately applied, this method also automatically ensures that the transform matrices of any ancestor nodes are also updated, if needed, before updating this node and its descendants.
Equivalent behaviour is invoked automatically during scheduled update processing between the invocations of the updateBeforeTransform: and updateAfterTransform: methods.
Changes that you make to the transform properties within the updateBeforeTransform: method will automatically be applied to the transformMatrix of the node. Because of this, it's best to make any changes to the transform properties in that method.
However, if you need to make changes to the transform properties in the updateAfterTransform: method of a node, after you have made all your changes to the node properties, you should then invoke this method on the node, in order to have those changes applied to the transformMatrix.
Similarly, if you have updated the transform properties of this node asynchronously through an event callback, and want those changes to be immediately reflected in the transform matrices, you can use this method to do so.
| - (void) updateTransformMatrix |
Applies the transform properties (location, rotation, scale) to the transformMatrix of this node, but NOT to any descendant nodes.
To ensure that the transforms are accurately applied, this method also automatically ensures that the transform matrices of any ancestor nodes are also updated, if needed, before updating this node and its descendants.
Use this method only when you know that you only need the transformMatrix of the specific node updated, and not the matrices of the decendants of that node, or if you will manually update the transformMatrices of the descendant nodes. If in doubt, use the updateTransformMatrices method instead.
| - (void) wasRemoved |
Template method that is invoked automatically when this node is removed from its parent node.
This implementation sets the isRunning property to NO. It also checks the value of the shouldCleanupWhenRemoved property and, if it is set to YES, stops and removes any CCActions running on this node.
| + (ccColor4F) wireframeBoxColor |
Returns the color that wireframe bounding boxes will be drawn in when created using the shouldDrawWireframeBox property.
Setting this property to kCCC4FBlackTransparent will cause the color of any new wireframe bounding boxes to be set to the value of the color property of the node instead.
The initial value of this class property is kCCC4FYellow.
Property Documentation
- (CC3Camera*) activeCamera [read, retain] |
If this node has been added to the 3D world, either directly, or as part of a node assembly, returns the activeCamera property of the CC3World instance, as accessed via the world property, otherwise returns nil.
Reading this property traverses up the node hierarchy. If this property is accessed frequently, it is recommended that it be cached.
Implemented in CC3World.
- (ccColor4F) ambientColor [read, write, assign] |
The ambient color of the materials of this node.
Setting this property sets the same property on all child nodes.
Querying this property returns the average value of querying this property on all child nodes. When querying this value on a large node assembly, be aware that this may be time-consuming.
Implemented in CC3Light, and CC3MeshNode.
- (CC3NodeAnimation *) animation [read, write, retain] |
The animation content of this node, which manages animating the node under the direction of a CC3Animate action.
To animate this node, set this property to an instance of a subclass of the abstract CC3NodeAnimation class, populated with animation data, and then create an instance of a CC3Animate action, and run it on this node.
- (ccBlendFunc) blendFunc [read, write, assign] |
Implementation of the CCBlendProtocol blendFunc property.
This is a convenience property that gets and sets the same property of the material of all descendant nodes
Querying this property returns the value of the same property from the first descendant node that supports materials, or {GL_ONE, GL_ZERO} if no descendant nodes support materials. Setting this property sets the same property on the materials in all descendant nodes.
Implemented in CC3MeshNode.
- (CC3BoundingBox) boundingBox [read, assign] |
Returns the smallest axis-aligned bounding box that surrounds any local content of this node, plus all descendants of this node.
The returned bounding box is specfied in the local coordinate system of this node.
Returns kCC3BoundingBoxNull if this node has no local content or descendants.
Since the bounding box of a node can change based on the locations, rotations, or scales of any descendant node, this property is measured dynamically on each access, by traversing all descendant nodes. This is a computationally expensive method.
- (CC3NodeBoundingVolume *) boundingVolume [read, write, retain] |
The bounding volume of this node.
This may be used by culling during drawing operations, or by physics simulations. Different shapes of boundaries are available, permitting tradeoffs between accuracy and computational processing time.
By default, nodes do not have a bounding volume. Subclasses may set a suitable bounding volume.
- (GLfloat) boundingVolumePadding [read, write, assign] |
Padding that is added to all edges of the bounding volume, when the bounding volume is automatically calculated, to ensure that all content is within the bounding volume.
The initial value of this property is zero.
- (CCArray *) children [read, assign] |
The child nodes of this node, in a node structural hierarchy.
- (ccColor3B) color [read, write, assign] |
Implementation of the CCRGBAProtocol color property.
Setting this property sets the same property on all child nodes.
Querying this property returns the average value of querying this property on all child nodes. When querying this value on a large node assembly, be aware that this may be time-consuming.
Implemented in CC3MeshNode.
- (BOOL) containsAnimation [read, assign] |
Indicates whether this node, or any of its descendants, contains an instance of an animation.
- (GLenum) depthFunction [read, write, assign] |
The depth function used by the GL engine when comparing the Z-distance of this node against previously drawn content.
This property only has effect if the shouldDisableDepthTest property is set to NO.
This property must be set to one of the following values:
- GL_LESS - the content of this node will be drawn if it is closer to the camera than previously drawn content.
- GL_LEQUAL - the content of this node will be drawn if it is at least as close to the camera as previously drawn content.
- GL_EQUAL - the content of this node will be drawn if it is exactly as close to the camera as previously drawn content.
- GL_GEQUAL - the content of this node will be drawn if it is at least as far away from the camera as previously drawn content.
- GL_GREATER - the content of this node will be drawn if it is farther away from the camera than previously drawn content.
- GL_NOTEQUAL - the content of this node will be drawn if it is not exactly as close to the camera as previously drawn content.
- GL_ALWAYS - the content of this node will always be drawn
- GL_NEVER - the content of this node will not be drawn
The initial value of this property is GL_LEQUAL. In most cases, to draw an accurate scene, this value is the most suitable. However, some special cases, including some particle emitters, may benefit from the use of one of the other depth functions.
Setting this value sets the same property on all descendant nodes.
Querying this property returns the value of this property from the first descendant mesh node, or will return GL_NEVER if no mesh node are found in the descendants of this node.
Implemented in CC3MeshNode.
- (CC3NodeDescriptor*) descriptorNode [read, assign] |
If the shouldDrawDescriptor is set to YES, returns the child node that draws the descriptor text on this node.
Otherwise, returns nil.
- (ccColor4F) diffuseColor [read, write, assign] |
The diffuse color of the materials of this node.
Setting this property sets the same property on all child nodes.
Querying this property returns the average value of querying this property on all child nodes. When querying this value on a large node assembly, be aware that this may be time-consuming.
Implemented in CC3Light, and CC3MeshNode.
- (CCArray*) directionMarkers [read, assign] |
Returns an array of all the direction marker child nodes that were previously added using the addDirectionMarkerColored:inDirection: and addDirectionMarker methods.
- (CC3Node*) dirtiestAncestor [read, assign] |
Returns the heighest node in my ancestor hierarchy, including myself, that is dirty.
Returns nil if neither myself nor any of my ancestors are dirty.
This method can be useful when deciding at what level to update a hierarchy.
This method is invoked automatically by the updateTransformMatrices and updateTransformMatrix, so in most cases, you do not need to use this method directly. However, there may be special cases where you want to determine beforehand whether this node or its ancestors are dirty or not before running either of those methods.
- (ccColor4F) emissionColor [read, write, assign] |
The emission color of the materials of this node.
Setting this property sets the same property on all child nodes.
Querying this property returns the average value of querying this property on all child nodes. When querying this value on a large node assembly, be aware that this may be time-consuming.
Implemented in CC3MeshNode.
- (CC3BoundingBox) globalBoundingBox [read, assign] |
Returns the smallest axis-aligned bounding box that surrounds any local content of this node, plus all descendants of this node.
The returned bounding box is specfied in the global coordinate system of the 3D world.
Returns kCC3BoundingBoxNull if this node has no local content or descendants.
Since the bounding box of a node can change based on the locations, rotations, or scales of any descendant node, this property is measured dynamically on each access, by traversing all descendant nodes. This is a computationally expensive method.
- (CC3Vector) globalLightLocation [read, write, assign] |
When a mesh node is textured with a DOT3 bump-map (normal map), this property indicates the location, in the global coordinate system, of the light that is illuminating the node.
When setting this property, this implementation sets the same property in all child nodes. Set the value of this property to the globalLocation of the light source. Bump-map textures may interact with only one light source.
This property only needs to be set, and will only have effect when set, on individual CC3MeshNodes whose material is configured for bump-mapping. This property is provided in CC3Node as a convenience to automatically traverse the node structural hierarchy to set this property in all descendant nodes.
When reading this property, this implementation returns the value of the same property from the first descendant node that is a CC3MeshNode and that contains a texture configured for bump-mapping. Otherwise, this implementation returns kCC3VectorZero.
Implemented in CC3MeshNode.
- (CC3Vector) globalLocation [read, assign] |
The location of the node in 3D space, relative to the global origin.
This is calculated by using the transformMatrix to translate the local origin (0,0,0).
- (CC3Vector) globalRotation [read, assign] |
Returns the overall rotation of the node in 3D space, relative to the global X, Y & Z axes.
The returned value contains three Euler angles, specified in degrees, defining a global rotation of this node around the X, Y and Z axes.
- (CC3Vector) globalScale [read, assign] |
The scale of the node in 3D space, relative to the global coordinate system, and accumulating the scaling of all ancestor nodes.
- (BOOL) hasLocalContent [read, assign] |
Indicates whether this node has local content that will be drawn.
Default value is NO. Subclasses that do draw content will override to return YES.
- (BOOL) hasSoftBodyContent [read, assign] |
Returns whether this structural node contains any descendant nodes that are used for soft-body vertex skinning.
This would include nodes of type CC3SkinMeshNode or CC3Bone.
This property is a convenience used to identify nodes that should be grouped together structurally under a CC3SoftBodyNode.
- (BOOL) isAnimationEnabled [read, write, assign] |
Indicates whether animation is enabled for this node.
This property only has effect if there the animation property is not nil.
The value of this property only applies to this node, not its child nodes. Child nodes that have this property set to YES will be animated even if this node has this property set to NO, and vice-versa.
Use the methods enableAllAnimation and disableAllAnimation to turn animation on or off for all the nodes in a node assembly.
The initial value of this property is YES.
- (BOOL) isBasePODNode [read, assign] |
Indicates whether this POD is a base node, meaning that it has no parent.
- (BOOL) isMeshNode [read, assign] |
Indicates whether this node has 3D mesh data to be drawn.
Default value is NO. Subclasses that do draw 3D meshes will override to return YES.
- (BOOL) isOpaque [read, write, assign] |
Indicates whether the content of this node and its descendants is opaque.
Returns NO if at least one descendant is not opaque, as determined by its isOpaque property. Returns YES if all descendants return YES from their isOpaque property.
Setting this property sets the same property in all descendants. See the notes for this property on CC3Material for more information on how this property interacts with the other material properties.
Setting this property should be thought of as a convenient way to switch between the two most common types of blending combinations. For finer control of blending, set specific blending properties on the CC3Material instance directly, and avoid making changes to this property.
Implemented in CC3MeshNode.
- (BOOL) isRunning [read, write, assign] |
Indicates whether the dynamic behaviour of this node is enabled.
Setting this property affects both internal activities driven by the update process, and any CCActions controling this node. Setting this property to NO will effectively pause all update and CCAction behaviour on the node. Setting this property to YES will effectively resume the update and CCAction behaviour.
Setting this property sets the same property in all descendant nodes.
Be aware that when this property is set to NO, any CCActions are just paused, but not stopped, or removed. If you want to fully stop all CCActions on this node, use the stopAllActions method, or if you want to fully stop all CCActions on this node AND all descendant nodes, use the cleanup method.
- (BOOL) isSkeletonRigid [read, assign] |
Returns whether the bones in this skeleton, at and above this bone, are rigid.
For the skeleton above a particular bone to be rigid, that bone node, and all nodes above that bone must have unity scaling, or must be within the tolerance value specified in the property of unity scaling.
This implementation tests whether this node has unity scaling (within the tolerance set in the property), and then queries whether the parent node of this node is also rigid. This propagates upwards in the structural hierarchy to the CC3SoftBodyNode, at the root of the skeleton.
Since the inverse transforms of the bones are relative to the CC3SoftBodyNode, if all nodes up to the CC3SoftBodyNode are rigid, then the skeleton is rigid.
- (BOOL) isTouchable [read, assign] |
Indicates whether this node will respond to UI touch events.
A node may often be touchable even if the isTouchEnabled flag is set to NO.
When the node is visible, this property returns YES under either of the following conditions:
- The isTouchEnabled property of this node is set to YES.
- The shouldInheritTouchability property of this node is set to YES, AND the isTouchable property of the parent of this node returns YES.
When the node is NOT visible, this property returns YES under either of the following conditions:
- The isTouchEnabled property of this node is set to YES AND the shouldAllowTouchableWhenInvisible is set to YES.
- The shouldInheritTouchability property of this node is set to YES, AND the isTouchable property of the parent of this node returns YES. AND the shouldAllowTouchableWhenInvisible of this node is set to YES.
This design simplifies identifying the node that is of interest when a touch event occurs. Thus, a car may be drawn as a node assembly of many descendant nodes (doors, wheels, body, etc). If isTouchEnabled is set for the car structural node, but not each wheel, it will be the parent car node that will be returned by the touchableNode property of the car structural node, or each wheel node. This allows the user to touch a wheel, but still have the car identified as the object of interest.
- (BOOL) isTouchEnabled [read, write, assign] |
Indicates if this node, or any of its descendants, will respond to UI touch events.
This property also affects which node will be returned by the touchableNode property. If the isTouchEnabled property is explicitly set for a parent node, but not for a child node, both the parent and the child can be touchable, but it will be the parent that is returned by the touchableNode property of either the parent or child.
This design simplifies identifying the node that is of interest when a touch event occurs. Thus, a car may be drawn as a node assembly of many descendant nodes (doors, wheels, body, etc). If isTouchEnabled is set for the car structural node, but not each wheel, it will be the parent car node that will be returned by the touchableNode property of the car structural node, or each wheel node. This allows the user to touch a wheel, but still have the car identified as the object of interest.
Normally, only visible nodes can be touched. But this can be changed by setting the shouldAllowTouchableWhenInvisible property to YES.
The initial value of this property is NO.
- (BOOL) isTransformDirty [read, assign] |
Indicates whether any of the transform properties, location, rotation, or scale have been changed, and so the transformMatrix of this needs to be recalculated.
This property is automatically set to YES when one of those properties have been changed, and is reset to NO once the transformMatrix has been recalculated.
Recalculation of the transformMatrix occurs automatically when the node is updated.
- (BOOL) isTransformRigid [read, assign] |
Returns whether the current transform applied to this node is rigid.
A rigid transform contains only rotation and translation transformations and does not include any scaling transformation. For the transform to be rigid, this node, and all ancestors of this node, must have unity scaling, or must be within the tolerance value specified in the property of unity scaling.
This implementation tests whether this node has unity scaling (within the tolerance set in the property), and then queries whether the parent node of this node is also rigid. This propagates upwards in the structural hierarchy, all the way to the root ancestor.
See the scaleTolerance property for more info on providing a tolerance to allow this evaluation to be fuzzy.
- (BOOL) isUniformlyScaledGlobally [read, assign] |
Indicates whether current global scaling (via the globalScale property) is uniform along all axes, within the tolerance value specified in the property, as tested against each ancestor independently.
This property takes into consideration the scaling of all ancestors.
- (BOOL) isUniformlyScaledLocally [read, assign] |
Indicates whether current local scaling (via the scale property) is uniform along all axes, within the tolerance value specified in the property.
This property does not take into consideration the scaling of any ancestors.
- (CC3Vector) location [read, write, assign] |
The location of the node in 3D space, relative to the parent of this node.
The global location of the node is therefore a combination of the global location of the parent of this node and the value of this location property.
- (CC3NormalScaling) normalScalingMethod [read, write, assign] |
Specifies the method to be used to scale vertex normals after they have been transformed during vertex drawing.
Normal vectors should have a unit length. Since normals are vectors in the local coordinate system of the node, they are transformed into world and eye coordinates during drawing.
During transformation, there are several factors that might distort the normal vector:
- If the normals started out not being of unit length, they will generally be transformed into vectors that are not of unit length.
- If the transforms are not rigid, and include scaling, even normals that have unit length in object space will end up shorter or longer than unit length in eye space.
- If the transform scaling is not uniform, the normals will shear, and end up shorter or longer than unit length.
Normals that are not of unit length, or are sheared, will cause portions of the objects to appear lighter or darker after transformation, or will cause specular highlights to actually be dark, distorting the overall look of the material covering the mesh.
The GL engine can be instructed to compensate for these transforms by setting this property as follows:
- kCC3NormalScalingNone: No compensating scaling is performed on the normals after they have been transformed. This has the highest performance, but will not adjust the normals if they have been scaled. Use this option if you know that the normals will not be significantly scaled during transformation.
- kCC3NormalScalingRescale: Uses the modelview matrix to scale all normals by the inverse of the node's overall scaling. This does have a processing cost, but is much faster than using kCC3NormalScalingNormalize. However, it is not as accurate if significantly non-uniform scaling has been applied to the node.
- kCC3NormalScalingNormalize: Normalizes each norml vector independently. This is the most accurate method, but is also, by far, the most computationally expensive. Use this method only if selecting one of the other options does not give you the results that you expect.
- kCC3NormalScalingAutomatic: Chooses the most appropriate method based on the scaling that has been applied to the node. If no scaling has been applied to the node, kCC3NormalScalingNone will be used. If only uniform scaling has been applied to the node, kCC3NormalScalingRescale will be used. If non-uniform scaling has been applied to the node, then kCC3NormalScalingNormalize will be used.
The initial value of this property is kCC3NormalScalingAutomatic. You can generally leave this property at this default value unless you are not getting the results that you expect.
Setting this property sets the corresponding property in all descendant nodes, and affects the processing of normals in all vertex meshes contained in all descendant nodes.
Querying this property returns the value of this property from the first descendant mesh node, or will return kCC3NormalScalingNone if no mesh node are found in the descendants of this node.
Implemented in CC3MeshNode.
- (GLubyte) opacity [read, write, assign] |
Implementation of the CCRGBAProtocol opacity property.
Querying this property returns the average value of querying this property on all child nodes. When querying this value on a large node assembly, be aware that this may be time-consuming.
Setting this property sets the same property in all descendants. See the notes for this property on CC3Material for more information on how this property interacts with the other material properties.
Setting this property should be thought of as a convenient way to switch between the two most common types of blending combinations. For finer control of blending, set specific blending properties on the CC3Material instance directly, and avoid making changes to this property.
Implemented in CC3MeshNode.
- (CC3Node *) parent [read, assign] |
The parent node of this node, in a node structural hierarchy.
- (CC3GLMatrix*) parentTransformMatrix [read, assign] |
Returns the transform matrix of the parent node.
Returns nil if there is no parent.
This template property is used by this class to base the transform of this node on the transform of its parent. A subclass may override to return nil if it determines that it wants to ignore the parent transform when calculating its own transform.
- (CC3PerformanceStatistics*) performanceStatistics [read, write, retain] |
Some node types (notably CC3World) collect runtime performance statistics using an instance of CC3PerformanceStatistics accessed by this property.
By default, nodes do not collect statistics. This property always returns nil, and setting this property has no effect. Subclasses that performance support statistics collection will override to allow the property to be get and set.
Implemented in CC3World.
- (int) podContentIndex [read, write, assign] |
The index of the POD data that forms the type-specific content of this node.
This is distinct from the podIndex property, which is the index of the data for the node, which may be of any node type. Once the type is established, the type-specific content is indexed by the podContentIndex property.
This abstract implementation does not map this property to an instance variable Concrete subclasses must override to map to an actual instance variable.
- (int) podParentIndex [read, write, assign] |
The index of the parent node of this node.
This will be -1 if this node has no parent.
This abstract implementation does not map this property to an instance variable Concrete subclasses must override to map to an actual instance variable.
- (CC3Vector) projectedLocation [read, write, assign] |
The current location of this node, as projected onto the 2D viewport coordinate space.
For most purposes, this is where this node will appear on the screen or window. The 2D position can be read from the X and Y components of the returned 3D location.
The initial value of this property is kCC3VectorZero. To set this property, pass this node as the argument to the projectNode: method of the active camera, which can be retrieved from the activeCamera property of the CC3World. The application should usually not set this property directly. For more information, see the notes for the projectNode: method of CC3Camera.
The Z-component of the returned location indicates the distance from the camera to this node, with a positive value indicating that this node is in front of the camera, and a negative value indicating that it is behind the camera. If you are only interested in the case when this node is in front of the camera (potentially visible to the camera), check that the Z-component of the returned location is positive.
When several nodes overlap a 2D position on the screen, you can also use the Z-component of the projectedLocation property of each of the nodes to determine which node is closest the camera, and is therefore "on-top" visually. This can be useful when trying to select a 3D node from an iOS touch event position.
The returned value takes into account the orientation of the device (portrait, landscape).
- (CGPoint) projectedPosition [read, assign] |
The current position of this node, as projected onto the 2D viewport coordinate space, returned as a 2D point.
For most purposes, this is where this node will appear on the screen or window.
This value is derived from the X and Y coordinates of the projectedLocation property. If this node is behind the camera, both the X and Y coordinates of the returned point will have the value -CGFLOAT_MAX.
The initial value of this property is CGPointZero. To set this property, pass this node as the argument to the projectNode: method of the active camera, which can be retrieved from the activeCamera property of the CC3World. For more information, see the notes for the projectNode: method of CC3Camera.
The returned value takes into account the orientation of the device (portrait, landscape).
- (CC3Vector4) quaternion [read, write, assign] |
The rotation of the node in 3D space, relative to the parent of this node, expressed as a quaternion.
Rotational transformation can also be specified using the rotation property (Euler angles), or the rotationAxis and rotationAngle properties. Subsequently, this property can be read to return the corresponding quaternion.
- (CC3Node*) rootAncestor [read, assign] |
Returns the root ancestor of this node, in the node structural hierarchy, or returns this node, if this node has no parent.
In almost all cases, this node returned will be the CC3World. However, if this node and all of its ancestors have not been added to the CC3World, then the returned node may be some other node.
Reading this property traverses up the node hierarchy. If this property is accessed frequently, it is recommended that it be cached.
- (CC3Vector) rotation [read, write, assign] |
The rotational orientation of the node in 3D space, relative to the parent of this node.
The global rotation of the node is therefore a combination of the global rotation of the parent of this node and the value of this rotation property. This value contains three Euler angles, defining a rotation of this nodearound the X, Y and Z axes. Each angle is specified in degrees.
Rotation is performed in Y-X-Z order, which is the OpenGL default. Depending on the nature of the object you are trying to control, you can think of this order as yaw, then pitch, then roll, or heading, then inclination, then tilt,
When setting this value, each component is converted to modulo +/-360 degrees.
Rotational transformation can also be specified using the rotationAxis and rotationAngle properties, or the quaternion property. Subsequently, this property can be read to return the corresponding Euler angles.
- (GLfloat) rotationAngle [read, write, assign] |
The angular rotation around the axis specified in the rotationAxis property.
Rotational transformation can also be specified using the rotation property (Euler angles), or the quaternion property. Subsequently, this property can be read to return the corresponding angle of rotation.
When setting this value, it is converted to modulo +/-360 degrees. When reading this value after making changes using rotateByAngle:aroundAxis:, or using another rotation property, the value of this property will be clamped to +/-180 degrees.
For example, if current rotation is 170 degrees around the rotationAxis, invoking the rotateByAngle:aroundAxis: method using the same rotation axis and 20 degrees, reading this property will return -170 degrees, not 190 degrees.
- (CC3Vector) rotationAxis [read, write, assign] |
The axis of rotation of the node in 3D space, relative to the parent of this node, expressed as a directional vector.
This axis can be used in conjunction with the rotationAngle property to describe the rotation as a single angular rotation around an arbitrary axis.
Under the identity rotation (no rotation), the rotationAngle is zero and the rotationAxis is undefined. Under that condition, this property will return the zero vector kCC3VectorZero.
Rotational transformation can also be specified using the rotation property (Euler angles), or the quaternion property. Subsequently, this property can be read to return the corresponding axis of rotation.
- (CC3Rotator *) rotator [read, assign] |
Returns the rotator that manages the local rotation of this node.
- (CC3Vector) scale [read, write, assign] |
The scale of the node in each dimension, relative to the parent of this node.
- (GLfloat) scaleTolerance [read, write, assign] |
Indicates a tolerance value that is used when testing scale component values, including testing whether a component value is close to unity (one), or whether two component values are close to each other (uniformity).
Exact unity scaling is useful because an unscaled (rigid) transform matrix can be inverted much faster than a scaled transform matrix, by a factor of between one and two orders of magnitude. If it is known that the transform matrix includes no scaling (has unity scaling), then the matrix will be inverted as a rigid matrix, to make use of this performance gain during inversion.
In addition, exact uniform scaling is useful when determining the method used to rescaling vertex normals during mesh transformations. The methods used if the transform includes no scaling, or if the transform includes only uniform scaling, are significantly faster than if the transform includes non-uniform scaling.
Although you can often deliberately set the scaling to exactly unity, or to be exactly uniform, there are some occasions, including animation and automatic physics, where the scale can be close to, but not exactly zero. By permitting a tolerance, unity scaling or uniform scaling can be assumed if the values are reasonably close, and the performance gain can be acquired under a wider range of conditions.
Specifically, the isTransformRigid will return YES if each of the X, Y & Z components of the scale property are within the tolerance range defined by this property, when comparing the components to unity.
For example, if the value of this property is 0.02, and the value of the scale property is (1.01, 1.0, 1.02), the isTransformRigid will return YES. However, if the value of this property was left at zero, the isTransformRigid property would return NO with the same scale value.
This property is also used by the isUniformlyScaledLocally and isUniformlyScaledGlobally properties when testing whether the components of the scale property are equal to each other, for the purpose of determining whether the scaling is uniform.
For example, if the value of this property is 0.02 and the value of the scale property is (3.01, 3.0, 3.02), the isUniformlyScaledLocally property will return YES, as will the isUniformlyScaledGlobally, if the ancestor scales are similarly uniform.
If this property is set to zero, then no tolerance is accepted, and all three components of the scale property must be exactly equal to one for this node to be considered to have no scaling applied, or exactly equal to each other for this node to be considered to have uniform scaling.
Setting this property sets the same property in all child nodes to the same value.
Initially, the value of this property is set to the value of the class-side defaultUnityScaleTolerance property. Use the class-side property to establish a global tolerance for all CC3Nodes.
- (BOOL) shouldAllowTouchableWhenInvisible [read, write, assign] |
Indicates whether this node should be touchable even when invisible.
When this property and the visible property are set to NO, the isTouchable property will always return NO. When this property is YES, the isTouchable property can return YES for an invisible node, if the other conditions for touchability are met. See the isTouchable property for more info.
The initial value of this propety is NO.
- (BOOL) shouldAutoremoveWhenEmpty [read, write, assign] |
Indicates whether this instance should automatically remove itself from its parent once its last child is removed.
Setting this property to YES can be useful for certain types of wrapper subclasses, where a instance wraps a single child node. Removing that child node from the node hierarchy (typically by invoking the remove method on that child node, and which may be performed automatically for some types of child nodes), will also cause the wrapper node to be removed as well. This cleanup is important to avoid littering your world with empty wrapper nodes.
The initial value of this property is NO, indicating that this instance will NOT automatically remove itself from the node hierarchy once all its child nodes have been removed.
- (BOOL) shouldCleanupWhenRemoved [read, write, assign] |
Indicates whether all the CCActions currently running on this node and all descendants should be stopped and removed when this node is removed from its parent.
If the value of this property is YES, when this node is removed from its parent, the cleanup method will automatically be invoked. If the value of this method is NO, when this node is removed from its parent, the isRunning property will be set to NO, which causes all actions to be paused, but not removed.
Stopping and removing CCActions is important because the actions running on a node retain links to the node. If the actions are simply paused, those links will be retained forever, potentially creating memory leaks of nodes that are invisibly retained by their actions.
The iniital value of this property is YES, indicating that all actions will be stopped and removed when this node is removed from its parent. If you have reason to want the actions to be paused but not removed when removing this node from its parent, set this property to NO.
One example of such a situation might be if you are moving a node from one parent to another. You may want to temporarily set this property to NO during the move so that the actions are paused during the move, but resumed when the node is added to a new parent.
If you have this property set to NO, you can manually stop and remove all actions using the cleanup method.
- (BOOL) shouldCullBackFaces [read, write, assign] |
Indicates whether the back faces should be culled on the meshes contained in descendants of this node.
The initial value is YES, indicating that back faces will not be displayed. You can set this property to NO if you have reason to display the back faces of the mesh (for instance, if you have a rectangular plane and you want to show both sides of it).
Since the normal of the face points out the front face, back faces interact with light the same way the front faces do, and will appear luminated by light that falls on the front face, much like a stained-glass window. This may not be the affect that you are after, and for some lighting conditions, instead of disabling back face culling, you might consider creating a second textured front face, placed back-to-back with the original front face.
Be aware that culling improves performance, so this property should be set to NO only when specifically needed for visual effect, and only on the meshes that need it.
Setting this value sets the same property on all descendant nodes.
Querying this property returns NO if any of the descendant mesh nodes have this property set to NO. Initially, and in most cases, all mesh nodes have this property set to YES.
For more information about this use of this property, see the class notes for the CC3MeshNode class.
Implemented in CC3MeshNode.
- (BOOL) shouldCullFrontFaces [read, write, assign] |
Indicates whether the front faces should be culled on the meshes contained in descendants of this node.
The initial value is NO. Normally, you should leave this property with the initial value, unless you have a specific need not to display the front faces.
Setting this value sets the same property on all descendant nodes.
Querying this property returns YES if any of the descendant mesh nodes have this property set to YES. Initially, and in most cases, all mesh nodes have this property set to NO.
For more information about this use of this property, see the class notes for the CC3MeshNode class.
Implemented in CC3MeshNode.
- (BOOL) shouldDisableDepthMask [read, write, assign] |
Indicates whether this instance will disable the GL depth mask while drawing the content of this node.
When the depth mask is disabled, drawing activity will not write to the depth buffer.
If this property is set to NO, the Z-distance of this node will be compared against previously drawn content, and the drawing of this node will update the depth buffer, so that subsequent drawing will take into consideration the Z-distance of this node.
If this property is set to YES, the Z-distance of this node will still be compared against previously drawn content, but the drawing of this node will NOT update the depth buffer, and subsequent drawing will NOT take into consideration the Z-distance of this node.
This property only has effect if the shouldDisableDepthTest property is set to NO.
In most cases, to draw an accurate scene, we want depth testing to be performed at all times, and this property is usually set to NO. However, there are some occasions where it is useful to disable writing to the depth buffer during the drawing of a node. One notable situation is with particle systems, where temporarily disabling the depth mask will avoid Z-fighting between individual particles.
The initial value of this property is NO, indicating that the GL depth mask will not be disabled during the drawing of this node, and the depth buffer will be updated during the drawing of this node.
Setting this value sets the same property on all descendant nodes.
Querying this property returns YES if any of the descendant mesh nodes have this property set to YES, otherwise returns NO.
Implemented in CC3MeshNode.
- (BOOL) shouldDisableDepthTest [read, write, assign] |
Indicates whether this instance will disable the GL depth test while drawing the content of this node.
When the depth test is disabled, the Z-distance of this node will not be compared against previously drawn content, and drawing activity will not write to the depth buffer.
If this property is set to NO, the Z-distance of this node will be compared against previously drawn content, and the drawing of this node will update the depth buffer, so that subsequent drawing will take into consideration the Z-distance of this node.
If this property is set to YES, the Z-distance of this node will not be compared against previously drawn content and this node will be drawn over all previously drawn content. In addition, the drawing of this node will not update the depth buffer, with the result that subsequent object drawing will not take into consideration the Z-distance of this node.
In most cases, to draw an accurate scene, we want depth testing to be performed at all times, and this property is usually set to NO. However, there are some occasions where it is useful to disable depth testing during the drawing of a node. One notable situation is with particle systems, where temporarily disabling depth testing may help avoid Z-fighting between individual particles.
The initial value of this property is NO, indicating that the GL depth tesing will not be disabled during the drawing of this node, and the depth buffer will be updated during the drawing of this node.
Setting this value sets the same property on all descendant nodes.
Querying this property returns YES if any of the descendant mesh nodes have this property set to YES, otherwise returns NO.
Implemented in CC3MeshNode.
- (BOOL) shouldDrawAllDescriptors [read, write, assign] |
Indicates the state of the shouldDrawDescriptor property of this node and all descendant nodes.
Setting this property sets that value into the shouldDrawDescriptor property on this and all descendant nodes.
Setting this property to YES draws a descriptor label on this node and each descendant node. Setting this property to NO removes all of those labels.
Reading this property traverses this node and its descendants and returns NO if any descendant returns NO. Otherwise returns YES.
- (BOOL) shouldDrawAllLocalContentWireframeBoxes [read, write, assign] |
Indicates the state of the shouldDrawLocalContentWireframeBox property of this node, if it has local content, and all descendant nodes that have local content.
Setting this property sets that value into the shouldDrawLocalContentWireframeBox property on this node, if it has local content, and all descendant nodes that have local content.
Setting this property to YES draws individual wireframe boxes around any local content of this node and any descendant nodes that have local content. Setting this property to NO removes all of those boxes.
Reading this property traverses this node and its descendants and returns NO if any descendant returns NO. Otherwise returns YES.
- (BOOL) shouldDrawAllWireframeBoxes [read, write, assign] |
Indicates the state of the shouldDrawWireframeBox property of this node and all descendant nodes.
Setting this property sets that value into the shouldDrawWireframeBox property on this and all descendant nodes.
Setting this property to YES draws individual wireframe boxes around this node and each descendant node. Setting this property to NO removes all of those boxes.
Reading this property traverses this node and its descendants and returns NO if any descendant returns NO. Otherwise returns YES.
If this node has no local content, or has descendant nodes without local content, or descendants themselves (for example cameras, lights, or simply empty structural or targetting nodes), setting this property will have no effect for those descendants. Under those conditions, it is possible to set this property to YES and subsequently read the property back as NO.
- (BOOL) shouldDrawDescriptor [read, write, assign] |
Indicates whether this node should display a descriptive label on this node.
When set to YES, a descriptive text label will appear on this node. The descriptive label is positioned at the origin of this node, in this node's local coordinate system. The origin is the pivot point around which transforms such as rotation, movement and scale will occur when applied to this node. The origin is not always the same as the center of geometry of the node.
The descriptive text will appear in the font size specified in the class-side descriptorFontSize property. The color of the descriptive text is determined by the subclass. Typically, for structural nodes, it is the same color as the wireframe box that is drawn around the node when the shouldDrawWireframeBox property is set to YES. For nodes with local content to draw, the color of the text is the same as the wireframe box that is drawn around the local content of the node when the shouldDrawLocalContentWireframeBox property is set to YES.
Setting this property to YES can be useful during development in determining the identification of visible nodes, or the location of nodes that are unable to be drawn correctly.
The descriptive label is drawn by creating and adding a CC3NodeDescriptor node as a child node to this node. CC3NodeDescriptor is a type of CC3Billboard, and is configured to contain a 2D CCLabel, whose text is set to the description of this node. Setting this property to YES adds the descriptor child node, and setting this property to NO removes the descriptor child node.
By default, the child descriptor node is not touchable, even if this node is touchable. If, for some reason you want the descriptor text to be touchable, you can retrieve the descriptor node from the descriptorNode property, and set the isTouchEnabled property to YES.
- (BOOL) shouldDrawWireframeBox [read, write, assign] |
Indicates whether the node should display a wireframe bounding box around this node and all its descendants.
The wireframe box is drawn by creating and adding a CC3WireframeBoundingBoxNode as a child node to this node. The dimensions of the child node are set from the boundingBox property of this node. Setting this property to YES adds the wireframe child node, and setting this property to NO removes the wireframe child node.
Setting this property to YES can be useful during development in determining the boundaries of a 3D structural node.
The color of the wireframe box will be the value of the class-side defaultWireframeBoxColor property, or the value of the color property of this node if defaultWireframeBoxColor is equal to kCCC4FBlackTransparent.
If this node has no local content, or no descendant nodes with local content, setting this property will have no effect. In this condition, it is possible to set this property to YES and subsequently read the property back as NO.
By default, the child wireframe node is not touchable, even if this node is touchable. If, for some reason you want the wireframe to be touchable, you can retrieve the wireframe node from the wireframeBoxNode property, and set the isTouchEnabled property to YES.
- (BOOL) shouldInheritTouchability [read, write, assign] |
Indicates whether this node should automatically be considered touchable if this node's parent is touchable.
By using this property, you can turn off touchability on a child node, even when the parent node is touchable.
Normally, a node will be touchable if its isTouchEnabled property is set to YES on the node itself, or on one of its ancestors. You can change this behaviour by setting this property to NO on the child node. With the isTouchEnabled property and this property both set to NO, the isTouchable property will return NO, even if the isTouchable property of the parent returns YES, and the node will not respond to touch events even if the parent node does.
The initial value of this property is YES, indicating that this node will return YES in the isTouchable property if the parent node returns YES in its isTouchable property, even if the isTouchEnabled property of this node is set to NO.
- (BOOL) shouldUseClockwiseFrontFaceWinding [read, write, assign] |
Indicates whether the edge-widing algorithm used by the GL engine to determine which face of a triangle is the front face should use clockwise winding.
If this property is set to YES, the front face of all triangles in the mesh of this node will be determined using clockwise winding of the edges. If this property is set to NO, the front face of all triangles in the mesh of this node will be determined using counter-clockwise winding of the edges.
The initial value of this property is NO, indicating that the OpenGL-standard counter-clockwise winding will be used by the GL engine to determine the front face of all triangles in the mesh of this node. Unless you have a reason to change this value, you should leave it at the initial value.
Setting this value sets the same property on all descendant nodes.
Querying this property returns YES if any of the descendant mesh nodes have this property set to YES, otherwise returns NO.
Implemented in CC3MeshNode.
- (BOOL) shouldUseFixedBoundingVolume [read, write, assign] |
Indicates whether the bounding volume of this node should be considered fixed, even if the mesh vertices that determine the boundary are changed, or should be recalculated whenever the underlying mesh vertices change.
If the value of this property is set to YES, the bounding volume will NOT be recalculated each time the vertices of the mesh are modified (typically via the setVertexLocation:at: method). If the value of this property is set to NO, the bounding volume will be recalculated each time the vertices of the mesh are modified.
The initial value of this property is NO, indicating that the bounding volume will be recalculated whenever the underlying mesh vertices change.
For most scenarios, the most accurate bounding volume is achieved by leaving setting this property to NO, and letting the bounding volume automatically adapt to changes in the underlying mesh vertices.
However, for some specialized meshes, such as particle generators, where the vertex data is continuously being modified in a predictable manner, the processing cost of constantly re-measuring the bounding volume may be significant, and it may be more effective to set a fixed bounding volume that encompasses the entire possible range of vertex location data, and set the value of this property to YES to stop the bounding volume from being recalculated every time the vertex data is changed.
See the note for the various subclasses of CC3NodeBoundingVolume (eg- CC3NodeBoundingBoxVolume and CC3NodeSphericalBoundingVolume) to learn how to set the properties of the bounding volumes, to fix them to a particular range.
- (BOOL) shouldUseLighting [read, write, assign] |
If this value is set to YES, current lighting conditions will be taken into consideration when drawing colors and textures, and the ambientColor, diffuseColor, specularColor, emissionColor, and shininess properties will interact with lighting settings.
If this value is set to NO, lighting conditions will be ignored when drawing colors and textures, and the material emissionColor will be applied to the mesh surface without regard to lighting. Blending will still occur, but the other material aspects, including ambientColor, diffuseColor, specularColor, and shininess will be ignored. This is useful for a cartoon effect, where you want a pure color, or the natural colors of the texture, to be included in blending calculations, without having to arrange lighting, or if you want those colors to be displayed in their natural values despite current lighting conditions.
Setting the value of this property sets the same property in the materials contained in all descendant nodes. Reading the value of this property returns YES if any descendant node returns YES, and returns NO otherwise.
Implemented in CC3MeshNode.
- (BOOL) shouldUseSmoothShading [read, write, assign] |
Indicates whether the shading of the faces of the mesh of this node should be smoothly shaded, using color interpolation between vertices.
If this property is set to YES, the color of each pixel in any face in the mesh of this node will be interpolated from the colors of all three vertices of the face, using the distance of the pixel to each vertex as the means to interpolate. The result is a smooth gradient of color across the face.
If this property is set to NO, the color of all pixels in any face in the mesh of this node will be determined by the color at the third vertex of the face. All pixels in the face will be painted in the same color.
The initial value is YES. For realistic rendering, you should leave this property with the initial value, unless you have a specific need to render flat color across each face in the mesh, such as to deliberately create a cartoon-like effect on the model.
Setting this value sets the same property on all descendant nodes.
Querying this property returns NO if any of the descendant mesh nodes have this property set to NO. Initially, and in most cases, all mesh nodes have this property set to YES.
Implemented in CC3MeshNode.
- (ccColor4F) specularColor [read, write, assign] |
The specular color of the materials of this node.
Setting this property sets the same property on all child nodes.
Querying this property returns the average value of querying this property on all child nodes. When querying this value on a large node assembly, be aware that this may be time-consuming.
Implemented in CC3Light, and CC3MeshNode.
- (NSString*) structureDescription [read, assign] |
Returns a description of the structure of this node and its descendants, by recursing through this node and its descendants and appending the result of the description property of each node.
The description of each node appears on a separate line and is indented according to its depth in the structural hierarchy, starting at this node.
- (CC3Node*) touchableNode [read, assign] |
Indicates the node that is of interest if this node is selected by a touch event.
The value of this property is not always this node, but may be an ancestor node instead.
The value returned by this property is this node if the isTouchEnabled property of this node is set to YES, or the nearest ancestor whose isTouchEnabled property is set to YES, or nil if neither this node, nor any ancestor has the isTouchEnabled property set to YES.
This design simplifies identifying the node that is of interest when a touch event occurs. Thus, a car may be drawn as a node assembly of many descendant nodes (doors, wheels, body, etc). If isTouchEnabled is set for the car structural node, but not each wheel, it will be the parent car node that will be returned by the touchableNode property of the car structural node, or each wheel node. This allows the user to touch a wheel, but still have the car identified as the object of interest.
- (CC3GLMatrix *) transformMatrix [read, write, retain] |
The transformation matrix derived from the location, rotation and scale transform properties of this node and any ancestor nodes.
This matrix is recalculated automatically when the node is updated.
The transformation matrix for each node is global, in that it includes the transforms of all ancestors to the node. This streamlines rendering in that it allows the transform of each drawable node to be applied directly, and allows the order in which drawable nodes are drawn to be independent of the node structural hierarchy.
Setting this property udpates the globalLocation and globalScale properties.
- (CC3GLMatrix *) transformMatrixInverted [read, assign] |
Returns the matrix inversion of the transformMatrix.
This can be useful for converting global transform properties, such as global location, rotation and scale to the local coordinate system of the node.
- (GLfloat) uniformScale [read, write, assign] |
The scale of the node, uniform in each dimension, relative to the parent of this node.
Unless non-uniform scaling is needed, it is preferable to use this property instead of the scale property.
If non-uniform scaling is applied via the scale property, this uniformScale property will return the length of the scale property vector divided by the length of a unit cube (sqrt(3.0)), as an approximation of the overall scaling condensed to a single scalar value.
- (BOOL) visible [read, write, assign] |
Controls whether this node shoud be displayed.
Initial value is YES.
You can set this to NO to make this node and all its descendants invisible to stop them from being displayed and to stop rendering processing on them.
When reading this property, the return value takes into consideration whether the parent is visible. As a result, setting this property to YES and then reading it may return NO if an ancestor has visibility set to NO.
- (CC3WireframeBoundingBoxNode*) wireframeBoxNode [read, assign] |
If the shouldDrawWireframeBox is set to YES, returns the child node that draws the wireframe box around this node.
Otherwise, returns nil.
- (CC3World*) world [read, assign] |
If this node has been added to the 3D world, either directly, or as part of a node assembly, returns the CC3World instance that forms the 3D world, otherwise returns nil.
Reading this property traverses up the node hierarchy. If this property is accessed frequently, it is recommended that it be cached.
- (GLint) zOrder [read, write, assign] |
Indicates the order in which this node should be drawn when compared to other nodes, when drawing order should be determined by distance from the camera (Z-order).
Sequencing nodes for drawing based on distance from the camera is necessary for translucent nodes.
In a drawing sequencer that sorts nodes by drawing order based on distance from the camera, the value of this property overrides the distances of the nodes from the camera. Sorting occurs on the value of this property first, and then on distance from the camera.
Sorting based on distance to the camera alone is quite effective. In almost all cases, it is not necessary to set the value of this property, and if nodes are moving around, setting a value to this property can actually interfere with the dynamic determination of the correct drawing order. Only use this property if you have reason to force a node to be drawn before or after another node for visual effect.
The smaller the value of this property, the closer to the camera the node is deemed to be. This property may be assigned a negative value.
The initial value of this property is zero.
The CC3World must be configured with a drawing sequencer that sorts by Z-order for this property to be effective.
This property only has effect for nodes with local content to draw (instances of CC3LocalContentNode). Setting this property passes the value to all descendant nodes. Reading this value returns the average value of all child nodes, or returns zero if there are no child nodes.
Implemented in CC3LocalContentNode.
The documentation for this class was generated from the following file:
 1.7.2
1.7.2